Understanding the effect of the HCV polymerase inhibitor mericitabine on early viral kinetics in the phase 2 JUMP-C and PROPEL studies
- PMID: 24602156
- PMCID: PMC4243904
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12369
Understanding the effect of the HCV polymerase inhibitor mericitabine on early viral kinetics in the phase 2 JUMP-C and PROPEL studies
Abstract
Aims: The aim was to evaluate early viral kinetics in patients receiving mericitabine [hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleoside polymerase inhibitor] with peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin in two clinical trials (PROPEL and JUMP-C).
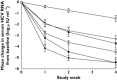
Methods: We examined rapid virological responses (RVRs; week 4 HCV RNA <15 IU ml(-1) ) and complete early virological responses (cEVR; week 12 HCV RNA <15 IU ml(-1) ) in HCV genotype 1/4-infected patients receiving mericitabine (500 or 1000 mg) or placebo twice daily plus peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin.
Results: Among IL28B rs12979860 CC genotype patients receiving 500 or 1000 mg mericitabine or placebo, respectively, RVR rates were 64.3% (95% confidence interval: 38.8-83.7%), 95.1% (83.9-98.7%) and 33.3% (20.2-49.7%), and cEVR rates were 100% (78.5-100%), 100% (91.4-100%) and 80.6% (65.0-90.3%). Among non-CC genotype patients, RVR rates were 26.5% (14.6-43.1%), 52.3% (43.0-61.3%) and 5.7% (2.2-13.8%), and cEVR rates were 76.5% (60.0-87.6%), 84.6% (76.6-90.1%) and 28.6% (19.3-40.1%), respectively. In multiple regression analysis, IL28B genotype (P < 0.0001), mericitabine dose (P < 0.0001) and bodyweight (P = 0.0009) were associated with first-phase (α) slope (change in log10 HCV RNA from baseline to week 1).
Conclusions: Mericitabine-containing triple therapy reduces the impact of IL28B genotype on RVR and cEVR compared with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin dual therapy. The IL28B genotype, mericitabine dose and bodyweight are the most important factors associated with the α slope, and there is no evidence of a pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction between mericitabine and ribavirin.
Keywords: hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitor; mericitabine; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; ribavirin.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

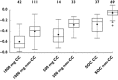
 , CC, merticitabine 500 mg bid (n = 15);
, CC, merticitabine 500 mg bid (n = 15);  , non-CC, merticitabine 500 mg bid (n = 34);
, non-CC, merticitabine 500 mg bid (n = 34);  , CC, merticitabine 1000 mg bid (n = 42);
, CC, merticitabine 1000 mg bid (n = 42);  , non-CC, merticitabine 1000 mg bid (n = 111);
, non-CC, merticitabine 1000 mg bid (n = 111);  , CC, placebo bid (n = 37);
, CC, placebo bid (n = 37);  , non-CC, placebo bid (n = 71)
, non-CC, placebo bid (n = 71)
 , mericitabine 500 mg bid plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin;
, mericitabine 500 mg bid plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin;  , mericitabine 1000 mg bid plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin;
, mericitabine 1000 mg bid plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin;  , placebo plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin
, placebo plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin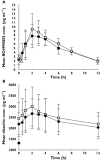
 , mericitabine 1000 mg bid + peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin (n = 59);
, mericitabine 1000 mg bid + peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin (n = 59);  , mericitabine 1000 mg bid monotherapy (n = 10); □, placebo bid + peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin (n = 35)
, mericitabine 1000 mg bid monotherapy (n = 10); □, placebo bid + peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin (n = 35)References
-
- Bacon BR, Gordon SC, Lawitz E, Marcellin P, Vierling JM, Zeuzem S, Poordad F, Goodman ZD, Sings HL, Boparai N, Burroughs M, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Esteban R HCV RESPOND-2 Investigators. Boceprevir for previously treated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1207–1217. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jacobson IM, McHutchison JG, Dusheiko G, Di Bisceglie AM, Reddy KR, Bzowej NH, Marcellin P, Muir AJ, Ferenci P, Flisiak R, George J, Rizzetto M, Shouval D, Sola R, Terg RA, Yoshida EM, Adda N, Bengtsson L, Sankoh AJ, Kieffer TL, George S, Kauffman RS, Zeuzem S ADVANCE Study Team. Telaprevir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2405–2416. - PubMed
-
- Poordad F, McCone J, Jr, Bacon BR, Bruno S, Manns MP, Sulkowski MS, Jacobson IM, Reddy KR, Goodman ZD, Boparai N, DiNubile MJ, Sniukiene V, Brass CA, Albrecht JK, Bronowicki JP SPRINT-2 Investigators. Boceprevir for untreated chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1195–1206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeuzem S, Andreone P, Pol S, Lawitz E, Diago M, Roberts S, Focaccia R, Younossi Z, Foster GR, Horban A, Ferenci P, Nevens F, Müllhaupt B, Pockros P, Terg R, Shouval D, van Hoek B, Weiland O, Van Heeswijk R, De Meyer S, Luo D, Boogaerts G, Polo R, Picchio G, Beumont M REALIZE Study Team. Telaprevir for retreatment of HCV infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2417–2428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

