Burden and predictors of hypertension in India: results of SEEK (Screening and Early Evaluation of Kidney Disease) study
- PMID: 24602391
- PMCID: PMC4015417
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-42
Burden and predictors of hypertension in India: results of SEEK (Screening and Early Evaluation of Kidney Disease) study
Abstract
Background: Hypertension (HTN) is one of the major causes of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. The objective of the study was to investigate the burden and predictors of HTN in India.
Methods: 6120 subjects participated in the Screening and Early Evaluation of Kidney disease (SEEK), a community-based screening program in 53 camps in 13 representative geographic locations in India. Of these, 5929 had recorded blood pressure (BP) measurements. Potential predictors of HTN were collected using a structured questionnaire for SEEK study.
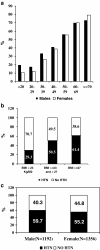
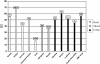
Results: HTN was observed in 43.5% of our cohort. After adjusting for center variation (p < 0.0001), predictors of a higher prevalence of HTN were older age ≥ 40 years (p < 0.0001), BMI of ≥ 23 Kg/M2 (p < 0.0004), larger waist circumference (p < 0.0001), working in sedentary occupation (p < 0.0001), having diabetes mellitus (p < 0.0001), having proteinuria (p < 0.0016), and increased serum creatinine (p < 0.0001). High school/some college education (p = 0.0016), versus less than 9th grade education, was related with lower prevalence of HTN. Of note, proteinuria and CKD were observed in 19% and 23.5% of HTN subjects. About half (54%) of the hypertensive subjects were aware of their hypertension status.
Conclusions: HTN was common in this cohort from India. Older age, BMI ≥ 23 Kg/M2, waist circumference, sedentary occupation, education less, diabetes mellitus, presence of proteinuria, and raised serum creatinine were significant predictors of hypertension. Our data suggest that HTN is a major public health problem in India with low awareness, and requires aggressive community-based screening and education to improve health.
Figures
References
-
- Murray CJ, Lauer JA, Hutubessy RC, Niessen L, Tomijima N, Rodgers A, Lawes CM, Evans DB. Effectiveness and costs of interventions to lower systolic blood pressure and cholesterol: a global and regional analysis on reduction of cardiovascular-disease risk. Lancet. 2003;361(9359):717–725. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12655-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The sixth report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157(21):2413–2446. - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD. Assessing the burden of mortality from cardiovascular diseases. World Health Stat Q. 1993;46(2):91–96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

