New roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in T cell biology: linking cell division and differentiation
- PMID: 24603166
- PMCID: PMC10114933
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3625
New roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in T cell biology: linking cell division and differentiation
Abstract
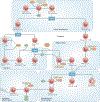
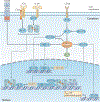
The proliferation of a few antigen-reactive lymphocytes into a large population of effector cells is a fundamental property of adaptive immunity. The cell division that fuels this process is driven by signals from antigen, co-stimulatory molecules and growth factor receptors, and is controlled by the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) cascade. In this Opinion article, we discuss how the CDK cascade provides one potential link between cell division and differentiation through the phosphorylation of immunologically relevant transcription factors, and how components of this pathway might ultimately participate in the decision between tolerance and immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of cyclin-dependent kinases in T-cell development, proliferation, and function.Crit Rev Immunol. 2006;26(3):189-212. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v26.i3.10. Crit Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16928186 Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinases: molecular switches controlling anergy and potential therapeutic targets for tolerance.Semin Immunol. 2007 Jun;19(3):173-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.02.009. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17383195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD28 costimulation mediates down-regulation of p27kip1 and cell cycle progression by activation of the PI3K/PKB signaling pathway in primary human T cells.J Immunol. 2002 Mar 15;168(6):2729-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2729. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11884439
-
A pathway regulated by cell cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 and checkpoint inhibitor Smad3 is involved in the induction of T cell tolerance.Nat Immunol. 2006 Nov;7(11):1157-65. doi: 10.1038/ni1398. Epub 2006 Oct 1. Nat Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17013388
-
B cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of cyclin-dependent retinoblastoma protein kinases and inhibition by co-cross-linking with Fc gamma receptors.J Immunol. 1999 Sep 15;163(6):3160-8. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10477583
Cited by
-
Immunomodulation by anticancer cell cycle inhibitors.Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Nov;20(11):669-679. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0300-y. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32346095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity is required for allogeneic T-cell responses after hematopoietic cell transplantation in mice.Blood. 2017 Jan 12;129(2):246-256. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-05-702738. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28064242 Free PMC article.
-
K48-linked KLF4 ubiquitination by E3 ligase Mule controls T-cell proliferation and cell cycle progression.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 13;8:14003. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14003. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28084302 Free PMC article.
-
The histone demethylase Lsd1 regulates multiple repressive gene programs during T cell development.J Exp Med. 2021 Dec 6;218(12):e20202012. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202012. Epub 2021 Nov 2. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34726730 Free PMC article.
-
Relieving Sore Throat Formula Exerts a Therapeutic Effect on Pharyngitis through Immunoregulation and NF-κB Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 May 15;2020:2929163. doi: 10.1155/2020/2929163. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32508523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lyons AB & Parish CR Determination of lymphocyte division by flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 171, 131–137 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

