New roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in T cell biology: linking cell division and differentiation
- PMID: 24603166
- PMCID: PMC10114933
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3625
New roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in T cell biology: linking cell division and differentiation
Abstract
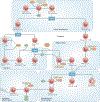
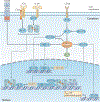
The proliferation of a few antigen-reactive lymphocytes into a large population of effector cells is a fundamental property of adaptive immunity. The cell division that fuels this process is driven by signals from antigen, co-stimulatory molecules and growth factor receptors, and is controlled by the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) cascade. In this Opinion article, we discuss how the CDK cascade provides one potential link between cell division and differentiation through the phosphorylation of immunologically relevant transcription factors, and how components of this pathway might ultimately participate in the decision between tolerance and immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lyons AB & Parish CR Determination of lymphocyte division by flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 171, 131–137 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

