The Sirt1 activator SRT3025 provides atheroprotection in Apoe-/- mice by reducing hepatic Pcsk9 secretion and enhancing Ldlr expression
- PMID: 24603306
- PMCID: PMC4286317
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu095
The Sirt1 activator SRT3025 provides atheroprotection in Apoe-/- mice by reducing hepatic Pcsk9 secretion and enhancing Ldlr expression
Abstract
Aims: The deacetylase sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) exerts beneficial effects on lipid metabolism, but its roles in plasma LDL-cholesterol regulation and atherosclerosis are controversial. Thus, we applied the pharmacological Sirt1 activator SRT3025 in a mouse model of atherosclerosis and in hepatocyte culture.
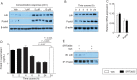
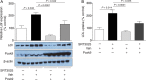
Methods and results: Apolipoprotein E-deficient (Apoe(-/-)) mice were fed a high-cholesterol diet (1.25% w/w) supplemented with SRT3025 (3.18 g kg(-1) diet) for 12 weeks. In vitro, the drug activated wild-type Sirt1 protein, but not the activation-resistant Sirt1 mutant; in vivo, it increased deacetylation of hepatic p65 and skeletal muscle Foxo1. SRT3025 treatment decreased plasma levels of LDL-cholesterol and total cholesterol and reduced atherosclerosis. Drug treatment did not change mRNA expression of hepatic LDL receptor (Ldlr) and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (Pcsk9), but increased their protein expression indicating post-translational effects. Consistent with hepatocyte Ldlr and Pcsk9 accumulation, we found reduced plasma levels of Pcsk9 after pharmacological Sirt1 activation. In vitro administration of SRT3025 to cultured AML12 hepatocytes attenuated Pcsk9 secretion and its binding to Ldlr, thereby reducing Pcsk9-mediated Ldlr degradation and increasing Ldlr expression and LDL uptake. Co-administration of exogenous Pcsk9 with SRT3025 blunted these effects. Sirt1 activation with SRT3025 in Ldlr(-/-) mice reduced neither plasma Pcsk9, nor LDL-cholesterol levels, nor atherosclerosis.
Conclusion: We identify reduction in Pcsk9 secretion as a novel effect of Sirt1 activity and uncover Ldlr as a prerequisite for Sirt1-mediated atheroprotection in mice. Pharmacological activation of Sirt1 appears promising to be tested in patients for its effects on plasma Pcsk9, LDL-cholesterol, and atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherogenesis; LDL receptor; LDL-cholesterol; Pcsk9; Sirt1.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sirtuin-1 directly binds and deacetylates hepatic PCSK9 thereby promoting the inhibition of LDL receptor degradation.Cardiovasc Res. 2025 Aug 14;121(9):1373-1384. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaf087. Cardiovasc Res. 2025. PMID: 40653676 Free PMC article.
-
PCSK9 inhibition fails to alter hepatic LDLR, circulating cholesterol, and atherosclerosis in the absence of ApoE.J Lipid Res. 2014 Nov;55(11):2370-9. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M053207. Epub 2014 Sep 25. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 25258384 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome Proliferator-activated receptor γ activation by ligands and dephosphorylation induces proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 and low density lipoprotein receptor expression.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23667-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.350181. Epub 2012 May 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22593575 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):1401-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.056. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23973703 Review.
-
On the function and homeostasis of PCSK9: reciprocal interaction with LDLR and additional lipid effects.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Feb;238(2):264-70. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.017. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 25544176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Theories and Molecular Basis of Vascular Aging: A Review of the Literature from VascAgeNet Group on Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Vascular Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8672. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158672. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 inhibition promotes atherosclerosis through impaired autophagy.Oncotarget. 2017 May 8;8(31):51447-51461. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17691. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881659 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting protein modifications in metabolic diseases: molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 27;8(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01439-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37244925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ageing induced vascular smooth muscle cell senescence in atherosclerosis.J Physiol. 2016 Apr 15;594(8):2115-24. doi: 10.1113/JP270923. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26174609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Nov;17(11):679-690. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.93. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27552971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gorenne I, Kumar S, Gray K, Figg N, Yu H, Mercer J, Bennett M. Vascular smooth muscle cell sirtuin 1 protects against DNA damage and inhibits atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2013;127:386–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

