Risk prediction of cardiovascular death based on the QTc interval: evaluating age and gender differences in a large primary care population
- PMID: 24603310
- PMCID: PMC4028611
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu081
Risk prediction of cardiovascular death based on the QTc interval: evaluating age and gender differences in a large primary care population
Abstract
Aims: Using a large, contemporary primary care population we aimed to provide absolute long-term risks of cardiovascular death (CVD) based on the QTc interval and to test whether the QTc interval is of value in risk prediction of CVD on an individual level.
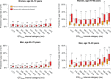
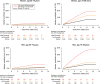
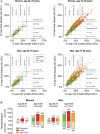
Methods and results: Digital electrocardiograms from 173 529 primary care patients aged 50-90 years were collected during 2001-11. The Framingham formula was used for heart rate-correction of the QT interval. Data on medication, comorbidity, and outcomes were retrieved from administrative registries. During a median follow-up period of 6.1 years, 6647 persons died from cardiovascular causes. Long-term risks of CVD were estimated for subgroups defined by age, gender, cardiovascular disease, and QTc interval categories. In general, we observed an increased risk of CVD for both very short and long QTc intervals. Prolongation of the QTc interval resulted in the worst prognosis for men whereas in women, a very short QTc interval was equivalent in risk to a borderline prolonged QTc interval. The effect of the QTc interval on the absolute risk of CVD was most pronounced in the elderly and in those with cardiovascular disease whereas the effect was negligible for middle-aged women without cardiovascular disease. The most important improvement in prediction accuracy was noted for women aged 70-90 years. In this subgroup, a total of 9.5% were reclassified (7.2% more accurately vs. 2.3% more inaccurately) within clinically relevant 5-year risk groups when the QTc interval was added to a conventional risk model for CVD.
Conclusion: Important differences were observed across subgroups when the absolute long-term risk of CVD was estimated based on QTc interval duration. The accuracy of the personalized CVD prognosis can be improved when the QTc interval is introduced to a conventional risk model for CVD.
Keywords: Cardiovascular death; Gender; Marquette 12SL validation; QTc interval; Risk prediction.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Using the electrocardiogram as a crystal ball for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality.Eur Heart J. 2014 May 21;35(20):1303-5. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu120. Epub 2014 Mar 30. Eur Heart J. 2014. PMID: 24685710 No abstract available.
References
-
- Morita H, Wu J, Zipes DP. The QT syndromes: long and short. Lancet. 2008;372:750–763. - PubMed
-
- Montanez A, Ruskin JN, Hebert PR, Lamas GA, Hennekens CH. Prolonged QTc interval and risks of total and cardiovascular mortality and sudden death in the general population: a review and qualitative overview of the prospective cohort studies. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:943–948. - PubMed
-
- Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren M, Albus C, Benlian P, Boysen G, Cifkova R, Deaton C, Ebrahim S, Fisher M, Germano G, Hobbs R, Hoes A, Karadeniz S, Mezzani A, Prescott E, Ryden L, Scherer M, Syvänne M, Scholte op Reimer WJM, Vrints C, Wood D, Zamorano JL, Zannad F European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR), ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012). The fifth joint task force of the European society of cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts) Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1635–1701. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen JB, Graff C, Pietersen A, Lind B, Struijk JJ, Olesen MS, Haunsø S, Gerds TA, Svendsen JH, Køber L, Holst AG. J-shaped association between QTc interval duration and the risk of atrial fibrillation: results from the Copenhagen ECG study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:2557–2564. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen JB, Pietersen A, Graff C, Lind B, Struijk JJ, Olesen MS, Haunsø S, Gerds TA, Ellinor PT, Køber L, Svendsen JH, Holst AG. Risk of atrial fibrillation as a function of the electrocardiographic PR interval: results from the Copenhagen ECG Study. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10:1249–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

