Innate immune activity conditions the effect of regulatory variants upon monocyte gene expression
- PMID: 24604202
- PMCID: PMC4064786
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1246949
Innate immune activity conditions the effect of regulatory variants upon monocyte gene expression
Abstract
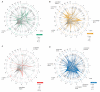
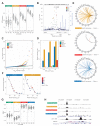
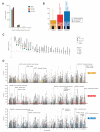
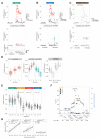
To systematically investigate the impact of immune stimulation upon regulatory variant activity, we exposed primary monocytes from 432 healthy Europeans to interferon-γ (IFN-γ) or differing durations of lipopolysaccharide and mapped expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs). More than half of cis-eQTLs identified, involving hundreds of genes and associated pathways, are detected specifically in stimulated monocytes. Induced innate immune activity reveals multiple master regulatory trans-eQTLs including the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), coding variants altering enzyme and receptor function, an IFN-β cytokine network showing temporal specificity, and an interferon regulatory factor 2 (IRF2) transcription factor-modulated network. Induced eQTL are significantly enriched for genome-wide association study loci, identifying context-specific associations to putative causal genes including CARD9, ATM, and IRF8. Thus, applying pathophysiologically relevant immune stimuli assists resolution of functional genetic variants.
Figures


Comment in
-
Genetics. A genomic road map for complex human disease.Science. 2014 Mar 7;343(6175):1087-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1251426. Science. 2014. PMID: 24604188 No abstract available.
-
Immunogenetics: tracking immune activity across the genome.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Apr;14(4):212. doi: 10.1038/nri3653. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24662379 No abstract available.
References
-
- Parkes M, Cortes A, van Heel DA, Brown MA. Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013;14:661–673. doi: 10.1038/nrg3502. - PubMed
-
- Emilsson V, et al. Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature. 2008;452:423–428. doi: 10.1038/nature06758. - PubMed
-
- Moffatt MF, et al. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature. 2007;448:470–473. doi: 10.1038/nature06014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

