Endoscopic innovations to increase the adenoma detection rate during colonoscopy
- PMID: 24605019
- PMCID: PMC3942825
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i9.2200
Endoscopic innovations to increase the adenoma detection rate during colonoscopy
Abstract
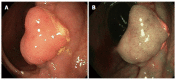
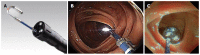
Up to a quarter of polyps and adenomas are missed during colonoscopy due to poor visualization behind folds and the inner curves of flexures, and the presence of flat lesions that are difficult to detect. These numbers may however be conservative because they mainly come from back-to-back studies performed with standard colonoscopes, which are unable to visualize the entire mucosal surface. In the past several years, new endoscopic techniques have been introduced to improve the detection of polyps and adenomas. The introduction of high definition colonoscopes and visual image enhancement technologies have been suggested to lead to better recognition of flat and small lesions, but the absolute increase in diagnostic yield seems limited. Cap assisted colonoscopy and water-exchange colonoscopy are methods to facilitate cecal intubation and increase patients comfort, but show only a marginal or no benefit on polyp and adenoma detection. Retroflexion is routinely used in the rectum for the inspection of the dentate line, but withdrawal in retroflexion in the colon is in general not recommended due to the risk of perforation. In contrast, colonoscopy with the Third-Eye Retroscope® may result in considerable lower miss rates compared to standard colonoscopy, but this technique is not practical in case of polypectomy and is more time consuming. The recently introduced Full Spectrum Endoscopy™ colonoscopes maintains the technical capabilities of standard colonoscopes and provides a much wider view of 330 degrees compared to the 170 degrees with standard colonoscopes. Remarkable lower adenoma miss rates with this new technique were recently demonstrated in the first randomized study. Nonetheless, more studies are required to determine the exact additional diagnostic yield in clinical practice. Optimizing the efficacy of colorectal cancer screening and surveillance requires high definition colonoscopes with improved virtual chromoendoscopy technology that visualize the whole colon mucosa while maintaining optimal washing, suction and therapeutic capabilities, and keeping the procedural time as low and patient discomfort as optimal as possible.
Keywords: Adenoma detection; Colonoscopy; Endoscopic innovations; Gastrointestinal endoscopy; Polyp detection.
Figures

References
-
- Jacob BJ, Moineddin R, Sutradhar R, Baxter NN, Urbach DR. Effect of colonoscopy on colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: an instrumental variable analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76:355–364.e1. - PubMed
-
- Lakoff J, Paszat LF, Saskin R, Rabeneck L. Risk of developing proximal versus distal colorectal cancer after a negative colonoscopy: a population-based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:1117–1121; quiz 1064. - PubMed
-
- Bressler B, Paszat LF, Chen Z, Rothwell DM, Vinden C, Rabeneck L. Rates of new or missed colorectal cancers after colonoscopy and their risk factors: a population-based analysis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:96–102. - PubMed
-
- le Clercq CM, Bouwens MW, Rondagh EJ, Bakker CM, Keulen ET, de Ridder RJ, Winkens B, Masclee AA, Sanduleanu S. Postcolonoscopy colorectal cancers are preventable: a population-based study. Gut. 2013:Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

