Connecticut (CCCRC) Olfactory Test: Normative Values in 426 Healthy Volunteers
- PMID: 24605298
- PMCID: PMC3938704
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-013-0632-z
Connecticut (CCCRC) Olfactory Test: Normative Values in 426 Healthy Volunteers
Abstract
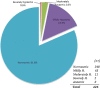
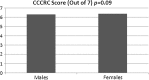
Application of Connecticut Chemosensory Clinical Research Center (CCCRC) olfactory test to healthy Turkish volunteers, obtain normative data set and analyse the role of age, sex and smoking on olfactory scores. The present study was conducted at Bezmialem Vakif University, Department of Otorhinolaryngology. Total of 426 healthy volunteers were subjected to CCCRC olfactory test which consists of n-butanol smell threshold test and smell identification test. Olfactory function score was assessed (0: worst score; 7: best score) and mean scores were calculated. Mean age was (36.7 ± 11.1; range, 17-68). 46.2 % of the subjects were male and 53.8 % were female; 37.1 % were smokers and 62.9 % were non-smokers. Mean n-butanol threshold score was 6.36 out of 7, mean identification score was 6.34 and mean total score was 6.35. According to CCCRC score: there were no anosmic individuals, 0.5 % were severely hyposmic, 2.6 % were moderately hyposmic,15.3 % were mildly hyposmic and 81.6 % were normosmic. CCCRC olfactory test is cost-effective, simple and practical. It can be easily applied in clinical settings. The CCCRC olfactory test is appropriate for assessment of olfactory function: Turkish population is familiar in terms of the odors used in CCCRC test. The power of this study is that it provides a normative data set against which many factors can be compared.
Keywords: CCCRC; Odor identification; Odor threshold; Olfactory dysfunction; Olfactory function; Olfactory test.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
