Efficacy, patient-reported outcomes and safety profile of ATX-101 (deoxycholic acid), an injectable drug for the reduction of unwanted submental fat: results from a phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 24605812
- PMCID: PMC4263247
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12377
Efficacy, patient-reported outcomes and safety profile of ATX-101 (deoxycholic acid), an injectable drug for the reduction of unwanted submental fat: results from a phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Background: Unwanted submental fat (SMF) may result in an unattractive chin profile and dissatisfaction with appearance. An approved and rigorously tested non-surgical method for SMF reduction is lacking.
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of ATX-101 for the pharmacological reduction of unwanted SMF in a phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Methods: Patients (n = 360) with moderate or severe SMF were randomized to receive ATX-101 1 or 2 mg/cm(2) or placebo injected into their SMF for up to four treatments ~28 days apart, with a 12-week follow-up. Coprimary efficacy endpoints were the proportions of treatment responders, defined as a ≥1-point reduction in SMF on the Clinician-Reported Submental Fat Rating Scale (CR-SMFRS), and those satisfied with their appearance in association with their face and chin after treatment on the Subject Self-Rating Scale (SSRS score ≥4). Secondary efficacy endpoints included a ≥1-point improvement in SMF on the Patient-Reported Submental Fat Rating Scale (PR-SMFRS) and changes in the Patient-Reported Submental Fat Impact Scale (PR-SMFIS). Additional patient-reported outcomes and changes in the Skin Laxity Rating Scale were recorded. Adverse events (AEs) and laboratory test results were monitored.
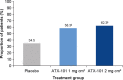
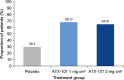
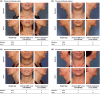
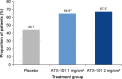
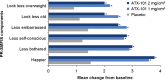
Results: Compared with placebo, a greater proportion of patients treated with ATX-101 1 and 2 mg/cm(2) showed a ≥1-point improvement in CR-SMFRS (58.3% and 62.3%, respectively, vs. 34.5% with placebo; P < 0.001) and patient satisfaction (SSRS score ≥4) with the appearance of their face and chin (68.3% and 64.8%, respectively, vs. 29.3%; P < 0.001). Patient-reported secondary efficacy endpoints showed significant improvements in SMF severity (PR-SMFRS; P = 0.009 for ATX-101 1 mg/cm(2) , P < 0.001 for ATX-101 2 mg/cm(2) vs. placebo) and emotions and perceived self-image (PR-SMFIS; P < 0.001). No overall worsening of skin laxity was observed. AEs were mostly transient, mild to moderate in intensity and localized to the treatment area.
Conclusion: ATX-101 was effective and well tolerated, and may be an alternative to surgery for patients desiring improvement of their submental profile.
© 2014 The Authors Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduction of unwanted submental fat with ATX-101 (deoxycholic acid), an adipocytolytic injectable treatment: results from a phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study.Br J Dermatol. 2014 Feb;170(2):445-53. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12695. Br J Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24147933 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Results from a pooled analysis of two European, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies of ATX-101 for the pharmacologic reduction of excess submental fat.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014 Oct;38(5):849-60. doi: 10.1007/s00266-014-0364-9. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2014. PMID: 24984785 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentered Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of MEI005 in Reducing Submental Fat in Chinese Adults.Aesthet Surg J. 2025 May 15;45(6):629-637. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjaf031. Aesthet Surg J. 2025. PMID: 40037621 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Deoxycholic Acid (ATX-101) for Reduction of Submental Fat.Ann Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;50(10):855-61. doi: 10.1177/1060028016653966. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Ann Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27340142 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of injectable deoxycholic acid for submental fat reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Mar;14(3):383-397. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2021.1884070. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33523775
Cited by
-
Management of Serious Adverse Events Following Deoxycholic Acid Injection for Submental and Jowl Fat Reduction: A Systematic Review and Management Recommendations.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2024 Aug 13;6:ojae061. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojae061. eCollection 2024. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2024. PMID: 39247122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Validation of a Photonumeric Scale for Assessment of Chin Retrusion.Dermatol Surg. 2016 Oct;42 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S211-S218. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000849. Dermatol Surg. 2016. PMID: 27661743 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of vitamin D receptor-mediated activities of cholesterol and vitamin D metabolites.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Feb 15;109:238-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26774929 Free PMC article.
-
Injection Adipocytolysis for Body and Jawline Contouring: Real-World Experience and Treatment Considerations.Aesthet Surg J. 2023 Mar 15;43(4):470-483. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjac285. Aesthet Surg J. 2023. PMID: 36326562 Free PMC article.
-
Lipolytic agents for submental fat reduction: Review.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Feb;30(2):e13601. doi: 10.1111/srt.13601. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 38297988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rzany B, Carruthers A, Carruthers J, et al. Validated composite assessment scales for the global face. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:294–308. - PubMed
-
- Ascher B. Developments in management of facial and body lipoatrophy with exogenous volumetric injectables. In: Landau M, Rossi B, editors. Injection Treatments in Cosmetic Surgery (Ascher B) London, UK: Informa Healthcare; 2008. pp. 329–338.
-
- Greco TM, Antunes MB, Yellin SA. Injectable fillers for volume replacement in the aging face. Facial Plast Surg. 2012;28:8–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

