A new model of LMP1-MYC interaction in B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 24605938
- PMCID: PMC4207734
- DOI: 10.3109/10428194.2014.900762
A new model of LMP1-MYC interaction in B cell lymphoma
Abstract
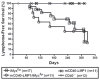
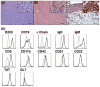
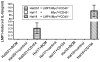
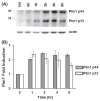
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with aggressive B cell lymphomas (BCLs). Latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) of EBV is an oncogenic protein required for EBV B cell transformation. However, LMP1 is a weak oncogene in mice. Mice expressing Myc inserted 5' of the Eμ enhancer (iMyc(Eμ)), mimicking the t(8;14) translocation of endemic Burkitt lymphoma, develop delayed onset BCLs. To investigate potential cooperation between LMP1 and oncogenic MYC, we produced mice expressing the LMP1 signaling domain via a hybrid CD40-LMP1 transgene (mCD40-LMP1), and the dysregulated MYC protein of aggressive EBV+ BCLs. mCD40-LMP1/iMyc(Eμ) mice trended toward earlier BCL onset. BCLs from mCD40-LMP1/iMyc(Eμ) mice expressed LMP1 and were transplantable into immunocompetent recipients. iMyc(Eμ) and mCD40-LMP1/iMyc(Eμ) mice developed BCLs with similar immunophenotypes. LMP1 signaling was intact in BCLs as shown by inducible interleukin-6. Additionally, LMP1 signaling to tumor cells induced the two isoforms of Pim1, a constitutively active prosurvival kinase implicated in lymphomagenesis.
Keywords: LMP1; MYC; lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Graham JP, Arcipowski KM, Bishop GA. Differential B-lymphocyte regulation by CD40 and its viral mimic, latent membrane protein 1. Immunol Rev. 2010;237:226–248. - PubMed
-
- Heslop HE. Biology and treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Prog. 2005:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Stunz LL, Busch LK, Munroe ME, et al. Expression of the cytoplasmic tail of LMP1 in mice induces hyperactivation of B lymphocytes and disordered lymphoid architecture. Immunity. 2004;21:255–266. - PubMed
-
- Rastelli J, Homig-Holzel C, Seagal J, et al. LMP1 signaling can replace CD40 signaling in B cells in vivo and has unique features of inducing class-switch recombination to IgG1. Blood. 2008;111:1448–1455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
