Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and replication
- PMID: 24606147
- PMCID: PMC4586249
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035428
Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and replication
Abstract
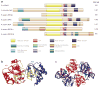
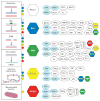
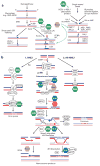
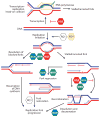
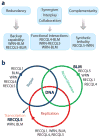
RecQ helicases are an important family of genome surveillance proteins conserved from bacteria to humans. Each of the five human RecQ helicases plays critical roles in genome maintenance and stability, and the RecQ protein family members are often referred to as guardians of the genome. The importance of these proteins in cellular homeostasis is underscored by the fact that defects in BLM, WRN, and RECQL4 are linked to distinct heritable human disease syndromes. Each human RecQ helicase has a unique set of protein-interacting partners, and these interactions dictate its specialized functions in genome maintenance, including DNA repair, recombination, replication, and transcription. Human RecQ helicases also interact with each other, and these interactions have significant impact on enzyme function. Future research goals in this field include a better understanding of the division of labor among the human RecQ helicases and learning how human RecQ helicases collaborate and cooperate to enhance genome stability.
Keywords: BLM; RECQL1; RECQL4; RECQL5; WRN; genome stability.
Figures
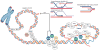
References
-
- Larsen NB, Hickson ID. RecQ helicases: conserved guardians of genomic integrity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;767:161–84. - PubMed
-
- Mandell JG, Goodrich KJ, Bahler J, Cech TR. Expression of a RecQ helicase homolog affects progression through crisis in fission yeast lacking telomerase. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:5249–57. - PubMed
-
- Barea F, Tessaro S, Bonatto D. In silico analyses of a new group of fungal and plant RecQ4-homologous proteins. Comput Biol Chem. 2008;32:349–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

