Ultrastructural characteristics of three undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem cell lines and their differentiated three-dimensional derivatives: a comparative study
- PMID: 24606239
- PMCID: PMC3967378
- DOI: 10.1089/cell.2013.0073
Ultrastructural characteristics of three undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem cell lines and their differentiated three-dimensional derivatives: a comparative study
Abstract
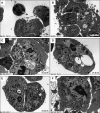
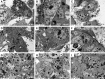
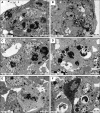
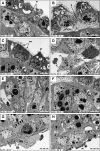
The fine structures of mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) grown as colonies and differentiated in three-dimensional (3D) culture as embryoid bodies (EBs) were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy. Undifferentiated mESCs expressed markers that proved their pluripotency. Differentiated EBs expressed different differentiation marker proteins from the three germ layers. The ultrastructure of mESCs revealed the presence of microvilli on the cell surfaces, large and deep infolded nuclei, low cytoplasm-to-nuclear ratios, frequent lipid droplets, nonprominent Golgi apparatus, and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. In addition, we found prominent juvenile mitochondria and free ribosomes-rich cytoplasm in mESCs. Ultrastructure of the differentiated mESCs as EBs showed different cell arrangements, which indicate the different stages of EB development and differentiation. The morphologies of BALB/c and 129 W9.5 EBs were very similar at day 4, whereas C57BL/6 EBs were distinct from the others at day 4. This finding suggested that differentiation of EBs from different cell lines occurs in the same pattern but not at the same rate. Conversely, the ultrastructure results of BALB/c and 129 W9.5 ESCs revealed differentiating features, such as the dilated profile of a rough endoplasmic reticulum. In addition, we found low expression levels of undifferentiated markers on the outer cells of BALB/c and 129 W9.5 mESC colonies, which suggests a faster differentiation potential.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ultrastructural comparison of porcine putative embryonic stem cells derived by in vitro fertilization and somatic cell nuclear transfer.J Reprod Dev. 2016 Apr 22;62(2):177-85. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2015-124. Epub 2016 Jan 28. J Reprod Dev. 2016. PMID: 26821870 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient differentiation of steroidogenic and germ-like cells from epigenetically-related iPSCs derived from ovarian granulosa cells.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 9;10(3):e0119275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119275. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25751620 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of calcium-sensing receptor in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) and its influence on differentiation of mESC into cardiomyocytes.Differentiation. 2013 Jan;85(1-2):32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2012.11.002. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Differentiation. 2013. PMID: 23314289
-
Gene expression profiles during early differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells.BMC Dev Biol. 2009 Jan 9;9:5. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-5. BMC Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19134196 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Ultrastructures of Primed and Naïve Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells.Cell Reprogram. 2016 Feb;18(1):48-53. doi: 10.1089/cell.2015.0063. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Cell Reprogram. 2016. PMID: 26757253
Cited by
-
Ultrastructural comparison of porcine putative embryonic stem cells derived by in vitro fertilization and somatic cell nuclear transfer.J Reprod Dev. 2016 Apr 22;62(2):177-85. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2015-124. Epub 2016 Jan 28. J Reprod Dev. 2016. PMID: 26821870 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria structural reorganization during mouse embryonic stem cell derivation.Protoplasma. 2018 Sep;255(5):1373-1386. doi: 10.1007/s00709-018-1236-y. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Protoplasma. 2018. PMID: 29549502
References
-
- Abe H., Yamashita S., Itoh T., Satoh T., and Hoshi H. (1999). Ultrastructure of bovine embryos developed from in vitro-matured and -fertilized oocytes: Comparative morphological evaluation of embryos cultured either in serum-free medium or in serum-supplemented medium. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 53, 325–335 - PubMed
-
- Baharvand H., and Matthaei K.I. (2003). The ultrastructure of mouse embryonic stem cells. Reprod. BioMed. Online 7, 330–335 - PubMed
-
- Baharvand H., Ashtiani S.K., Valojerdi M.R., Shahverdi A., Taee A., and Sabour D. (2004). Establishment and in vitro differentiation of a new embryonic stem cell line from human blastocyst. Differentiation 72, 224–229 - PubMed
-
- Bongso A., and Richards M. (2004). History and perspective of stem cell research. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 18, 827–842 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

