Survival analyses correlate stanniocalcin 2 overexpression to poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinomas
- PMID: 24606961
- PMCID: PMC4015363
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-26
Survival analyses correlate stanniocalcin 2 overexpression to poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Abstract
Background: Stanniocalcin 2 (STC2) is overexpressed in several types of human cancers, and its overexpression positively correlates to tumor progression and poor prognosis. However, the clinical significance of STC2 overexpression in nasopharyngeal carcinomas (NPC) has not been investigated. This study examined STC2 expression in a cohort of 94 NPC samples, and explored its value in clinical diagnosis and prognosis.
Methods: Tumor samples from 94 patients diagnosed in 2008 were studied. All samples were obtained prior to treatment start. All cases were clinically diagnosed and pathologically confirmed to be poorly differentiated or undifferentiated NPC without distant metastasis, and have been treated with radical radiation therapy and followed-up for five years. Survival analyses were performed.
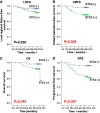
Results: Of the 94 NPC samples, STC2 overexpression (STC2+) was detected in 65 samples (69.1%). Overall survival rate of STC2 (+) patients is significantly lower than that of patients with normal STC2 levels (72.2% vs. 96.4%, respectively, P = 0.049). Moreover, STC2 (+) is also strongly predictive of a low progression-free survival and distant metastasis-free survival (63.0% vs 92.9%. P = 0.007; and 77.0% vs 96.4%. P = 0.028). Of the 54 patients treated with IMRT, residual tumors were found in 54.8% of STC2 positive patients (17/31), but only in 17.4% of STC2 negative ones (4/23), suggesting STC2 overexpression predicts a higher risk of residual tumors after IMRT.
Conclusions: STC2 overexpression correlates to poor prognosis for NPC and may be useful as a novel biomarker to predict NPC responses to radiation. Whether STC2 promotes NPC progression and metastasis remains to be investigated.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation of PD-L1 Expression of Tumor Cells with Survival Outcomes after Radical Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy for Non-Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 24;11(6):e0157969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157969. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27341634 Free PMC article.
-
Stanniocalcin-2 promotes cell EMT and glycolysis via activating ITGB2/FAK/SOX6 signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022 Apr;38(2):259-272. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09600-5. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 33797657 Free PMC article.
-
Stanniocalcin 2 expression is associated with a favourable outcome in male breast cancer.J Pathol Clin Res. 2018 Oct;4(4):241-249. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.106. Epub 2018 Aug 23. J Pathol Clin Res. 2018. PMID: 29956502 Free PMC article.
-
Stanniocalcin 2 (STC2): a universal tumour biomarker and a potential therapeutical target.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 May 2;41(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02370-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35501821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals the Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Value of Stanniocalcin-2 (STC2).Front Genet. 2022 Jul 22;13:927046. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.927046. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35937984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stanniocalcin 2 governs cancer cell adaptation to nutrient insufficiency through alleviation of oxidative stress.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Aug 6;15(8):567. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06961-7. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39107307 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Stanniocalcin 2 in Breast Cancer and Its Clinical Significance.Curr Med Sci. 2019 Dec;39(6):978-983. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2131-2. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Curr Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31845230
-
STC2 Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer and Promotes Migration and Invasion by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 15;2019:8042489. doi: 10.1155/2019/8042489. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 32258098 Free PMC article.
-
SNHG17 Serves as an Oncogenic lncRNA by Regulating the miR-361-3p/STC2 Axis in Rectal Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 23;12:654686. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.654686. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34249085 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of XRCC6 Promotes Human Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation through the β-Catenin/Wnt Signaling Pathway and Is Associated with Poor Prognosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 22;17(7):1188. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071188. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27455247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, Forastiere AA, Adams G, Sakr WA, Schuller DE, Ensley JF. Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Phase III randomized intergroup study 0099. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(4):1310–1317. - PubMed
-
- Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, Forastiere AA, Adams G, Sakr WA, Schuller DE, Ensley JF. Superiority of 5-year survival with chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal cancer. Intergroup 0099 Phase III study: final report [Abstract] Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2001;20:227a.
-
- Hareyama M, Sakata K, Shirato H, Nishioka T, Nishio M, Suzuki K, Saitoh A, Oouchi A, Fukuda S, Himi T. Prospective, randomized trial comparing neoadjuvant chemotherapy with radiotherapy alone in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;94(8):2217–2223. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10473. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chi KH, Chang YC, Guo WY, Leung MJ, Shiau CY, Chen SY, Wang LW, Lai YL, Hsu MM, Lian SL, Chang CH, Liu TW, Chin YH, Yen SH, Perng CH, Chen KY. A phase III study of adjuvant chemotherapy in advanced stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;52(5):1238–1244. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(01)02781-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

