The clinical course of low back pain: a meta-analysis comparing outcomes in randomised clinical trials (RCTs) and observational studies
- PMID: 24607083
- PMCID: PMC4007531
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-68
The clinical course of low back pain: a meta-analysis comparing outcomes in randomised clinical trials (RCTs) and observational studies
Abstract
Background: Evidence suggests that the course of low back pain (LBP) symptoms in randomised clinical trials (RCTs) follows a pattern of large improvement regardless of the type of treatment. A similar pattern was independently observed in observational studies. However, there is an assumption that the clinical course of symptoms is particularly influenced in RCTs by mere participation in the trials. To test this assumption, the aim of our study was to compare the course of LBP in RCTs and observational studies.
Methods: Source of studies CENTRAL database for RCTs and MEDLINE, CINAHL, EMBASE and hand search of systematic reviews for cohort studies. Studies include individuals aged 18 or over, and concern non-specific LBP. Trials had to concern primary care treatments. Data were extracted on pain intensity. Meta-regression analysis was used to compare the pooled within-group change in pain in RCTs with that in cohort studies calculated as the standardised mean change (SMC).
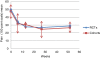
Results: 70 RCTs and 19 cohort studies were included, out of 1134 and 653 identified respectively. LBP symptoms followed a similar course in RCTs and cohort studies: a rapid improvement in the first 6 weeks followed by a smaller further improvement until 52 weeks. There was no statistically significant difference in pooled SMC between RCTs and cohort studies at any time point:- 6 weeks: RCTs: SMC 1.0 (95% CI 0.9 to 1.0) and cohorts 1.2 (0.7to 1.7); 13 weeks: RCTs 1.2 (1.1 to 1.3) and cohorts 1.0 (0.8 to 1.3); 27 weeks: RCTs 1.1 (1.0 to 1.2) and cohorts 1.2 (0.8 to 1.7); 52 weeks: RCTs 0.9 (0.8 to 1.0) and cohorts 1.1 (0.8 to 1.6).
Conclusions: The clinical course of LBP symptoms followed a pattern that was similar in RCTs and cohort observational studies. In addition to a shared 'natural history', enrolment of LBP patients in clinical studies is likely to provoke responses that reflect the nonspecific effects of seeking and receiving care, independent of the study design.
Figures

References
-
- Machado LAC, Kamper SJ, Herbert RD, Maher CG, MacAuley JH. Analgesic effects of treatments for non-specific low back pain: a meta-analysis of placebo controlled randomized trials. Rheumatology. 2009;48:520–527. - PubMed
-
- Artus M, van der Windt DA, Jordan KP, Hay EM. Low back pain symptoms show a similar pattern of improvement following a wide range of primary care treatments: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Rheumatology. 2012;49:2346–2356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

