Dietary and metabolic control of stem cell function in physiology and cancer
- PMID: 24607404
- PMCID: PMC3992244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.02.008
Dietary and metabolic control of stem cell function in physiology and cancer
Abstract
Organismal diet has a profound impact on tissue homeostasis and health in mammals. Adult stem cells are a keystone of tissue homeostasis that alters tissue composition by balancing self-renewal and differentiation divisions. Because somatic stem cells may respond to shifts in organismal physiology to orchestrate tissue remodeling and some cancers are understood to arise from transformed stem cells, there is a likely possibility that organismal diet, stem cell function, and cancer initiation are interconnected. Here we will explore the emerging effects of diet on nutrient-sensing pathways active in mammalian tissue stem cells and their relevance to normal and cancerous growth.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


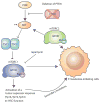
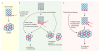
References
-
- Barker N, Huch M, Kujala P, van de Wetering M, Snippert HJ, van Es JH, Sato T, Stange DE, Begthel H, van den Born M, et al. Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell stem cell. 2010;6:25–36. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR, Sansom OJ, Clevers H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature. 2009;457:608–611. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Oudenaarden A, Clevers H. Identifying the stem cell of the intestinal crypt: strategies and pitfalls. Cell stem cell. 2012;11:452–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG045144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI047389/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI047389/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG045144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA129105/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129105/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047389/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA103866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA103866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG045144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

