Localization and interaural time difference (ITD) thresholds for cochlear implant recipients with preserved acoustic hearing in the implanted ear
- PMID: 24607490
- PMCID: PMC4036440
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2014.02.007
Localization and interaural time difference (ITD) thresholds for cochlear implant recipients with preserved acoustic hearing in the implanted ear
Abstract
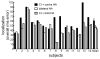
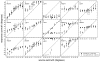
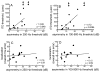
The purpose of this study was to investigate horizontal plane localization and interaural time difference (ITD) thresholds for 14 adult cochlear implant recipients with hearing preservation in the implanted ear. Localization to broadband noise was assessed in an anechoic chamber with a 33-loudspeaker array extending from -90 to +90°. Three listening conditions were tested including bilateral hearing aids, bimodal (implant + contralateral hearing aid) and best aided (implant + bilateral hearing aids). ITD thresholds were assessed, under headphones, for low-frequency stimuli including a 250-Hz tone and bandpass noise (100-900 Hz). Localization, in overall rms error, was significantly poorer in the bimodal condition (mean: 60.2°) as compared to both bilateral hearing aids (mean: 46.1°) and the best-aided condition (mean: 43.4°). ITD thresholds were assessed for the same 14 adult implant recipients as well as 5 normal-hearing adults. ITD thresholds were highly variable across the implant recipients ranging from the range of normal to ITDs not present in real-world listening environments (range: 43 to over 1600 μs). ITD thresholds were significantly correlated with localization, the degree of interaural asymmetry in low-frequency hearing, and the degree of hearing preservation related benefit in the speech reception threshold (SRT). These data suggest that implant recipients with hearing preservation in the implanted ear have access to binaural cues and that the sensitivity to ITDs is significantly correlated with localization and degree of preserved hearing in the implanted ear.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

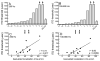

References
-
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Specifications for Audiometers (ANSI/ASA S3.6-2010) New York, NY: 2010.
-
- Bronkhorst AW, Plomp R. Binaural speech intelligibility in noise for hearing-impaired listeners. J Acoust Soc Am. 1989;86:1374–1383. - PubMed
-
- Dillon H, Katsch R, Byrne D, Ching T, Keidser G, Brewer S. National Acoustics Laboratories Research and Development, Annual Report 1997/98. National Acoustics Laboratories; Sydney, Australia: 1998. The NAL-NL1 Prescription Procedure for Non-linear Hearing Aids; pp. 4–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

