Age-related brain expression and regulation of the chemokine CCL4/MIP-1β in APP/PS1 double-transgenic mice
- PMID: 24607962
- PMCID: PMC3977177
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000060
Age-related brain expression and regulation of the chemokine CCL4/MIP-1β in APP/PS1 double-transgenic mice
Abstract
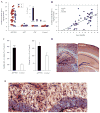
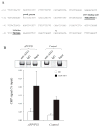
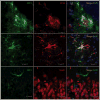
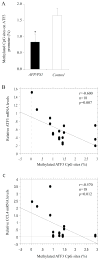
The detrimental effect of activation of the chemokine CCL4/MIP-1β on neuronal integrity in patients with HIV-associated dementia has directed attention to the potential role of CCL4 expression and regulation in Alzheimer disease. Here, we show that CCL4 mRNA and protein are overexpressed in the brains of APPswe/PS1ΔE9 (APP/PS1) double-transgenic mice, a model of cerebral amyloid deposition; expression was minimal in brains from nontransgenic littermates or single-mutant controls. Increased levels of CCL4 mRNA and protein directly correlated with the age-related progression of cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ) levels in APP/PS1 mice. We also found significantly increased expression of activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), which was positively correlated with age-related Aβ deposition and CCL4 in the brains of APP/PS1 mice. Results from chromatin immunoprecipitation-quantitative polymerase chain reaction confirmed that ATF3 binds to the promoter region of the CCL4 gene, consistent with a potential role in regulating CCL4 transcription. Finally, elevated ATF3 mRNA expression in APP/PS1 brains was associated with hypomethylation of the ATF3 gene promoter region. These observations prompt the testable hypothesis for future study that CCL4 overexpression, regulated in part by hypomethylation of the ATF3 gene, may contribute to neuropathologic progression associated with amyloid deposition in Alzheimer disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicting financial interests with regard to the current study.
Figures


References
-
- Gorelick PB. Role of inflammation in cognitive impairment: results of observational epidemiological studies and clinical trials. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1207:155–62. - PubMed
-
- Perry VH, Cunningham C, Holmes C. Systemic infections and inflammation affect chronic neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:161–7. - PubMed
-
- Minagar A, Shapshak P, Fujimura R, et al. The role of macrophage/microglia and astrocytes in the pathogenesis of three neurologic disorders: HIV-associated dementia, Alzheimer disease, and multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2002;202:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Schmidtmayerova H, Nottet HS, Nuovo G, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection alters chemokine beta peptide expression in human monocytes: implications for recruitment of leukocytes into brain and lymph nodes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1996;93:700–4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kelder W, McArthur JC, Nance-Sproson T, et al. Beta-chemokines MCP-1 and RANTES are selectively increased in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:831–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

