Rapid and accurate identification by real-time PCR of biotoxin-producing dinoflagellates from the family gymnodiniaceae
- PMID: 24608972
- PMCID: PMC3967215
- DOI: 10.3390/md12031361
Rapid and accurate identification by real-time PCR of biotoxin-producing dinoflagellates from the family gymnodiniaceae
Abstract
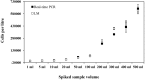
The identification of toxin-producing dinoflagellates for monitoring programmes and bio-compound discovery requires considerable taxonomic expertise. It can also be difficult to morphologically differentiate toxic and non-toxic species or strains. Various molecular methods have been used for dinoflagellate identification and detection, and this study describes the development of eight real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays targeting the large subunit ribosomal RNA (LSU rRNA) gene of species from the genera Gymnodinium, Karenia, Karlodinium, and Takayama. Assays proved to be highly specific and sensitive, and the assay for G. catenatum was further developed for quantification in response to a bloom in Manukau Harbour, New Zealand. The assay estimated cell densities from environmental samples as low as 0.07 cells per PCR reaction, which equated to three cells per litre. This assay not only enabled conclusive species identification but also detected the presence of cells below the limit of detection for light microscopy. This study demonstrates the usefulness of real-time PCR as a sensitive and rapid molecular technique for the detection and quantification of micro-algae from environmental samples.
Figures


References
-
- Daugbjerg N., Hansen G., Larsen J., Moestrup O. Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates. Phycologia. 2000;39:302–317. doi: 10.2216/i0031-8884-39-4-302.1. - DOI
-
- de Salas M.F., Bolch C.J.S., Botes L., Nash G., Wright S.W., Hallegraeff G.M. Takayama gen. nov (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae), a new genus of unarmored dinoflagellates with sigmoid apical grooves, including the description of two new species. J. Phycol. 2003;39:1233–1246. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.2003.03-019.x. - DOI
-
- Taylor F.J.R., Fukuyo Y., Larsen J., Hallegraeff G.M. Taxonomy of Harmful Dinoflagellates. In: Hallegraeff G.M., Anderson D.M., Cembella A.D., editors. Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae. UNESCO Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission; Pairs, France: 2003. pp. 389–432.
-
- Rhodes L.L., Haywood A.J., Ballantine W.J., MacKenzie A.L. Algal blooms and climate anomalies in north-east New Zealand, August–December 1992. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1993;27:419–430. doi: 10.1080/00288330.1993.9516583. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

