Prognosis of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of seven staging systems (TNM, Okuda, BCLC, CLIP, CUPI, JIS, CIS) in a Chinese cohort
- PMID: 24609114
- PMCID: PMC3946426
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088182
Prognosis of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of seven staging systems (TNM, Okuda, BCLC, CLIP, CUPI, JIS, CIS) in a Chinese cohort
Abstract
Background: Many liver staging systems that include the tumor stage and the extent of liver function have been developed. However, prognosis assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains controversial. In this study, the performances of 7 staging systems were compared in a cohort of patients with HCC who underwent non-surgical treatment.
Methods: A total of 196 consecutive patients with HCC who underwent non-surgical treatment seen between January 1, 2004, and December 31, 2007, were included. Performances of TNM sixth edition, Okuda, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC), Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP), Chinese University Prognostic Index (CUPI), Japan Integrated Staging (JIS), and China integrated score (CIS) have been compared and ranked using concordance index (c-index). Predictors of survival were identified using univariate and multivariate Cox model analyses.
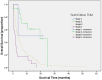
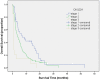
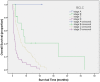
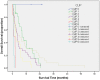
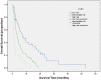
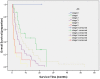
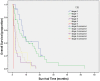
Results: The median survival time for the cohort was 7.6 months (95% CI 5.6-9.7). The independent predictors of survival were performance status (P<.001), serum sodium (P<.001), alkaline phosphatase (P<.001), tumor diameter greater than 5 cm (P = .001), portal vein invasion (P<.001), lymph node metastasis (P = .025), and distant metastasis (P = .004). CUPI staging system had the best independent predictive power for survival when compared with the other six prognostic systems. Performance status and serum sodium improved the discriminatory ability of CUPI.
Conclusion: In our selected patient population whose main etiology is hepatitis B, CUPI was the most suitable staging system in predicting survival in patients with unresectable HCC. BCLC was the second top-ranking staging system. CLIP, JIS, CIS, and TNM sixth edition were not helpful in predicting survival outcome, and their use is not supported by our data.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation and ranking of seven staging systems of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):705-714. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6222. Epub 2017 May 22. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693224 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: which staging systems best predict prognosis?J Clin Oncol. 2010 Jun 10;28(17):2889-95. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.9895. Epub 2010 May 10. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20458042 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of the Chinese University Prognostic Index for hepatocellular carcinoma and comparison with the TNM staging system, the Okuda staging system, and the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program staging system: a study based on 926 patients.Cancer. 2002 Mar 15;94(6):1760-9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10384. Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11920539 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma (CLIP score): its value and limitations, and a proposal for a new staging system, the Japan Integrated Staging Score (JIS score).J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(3):207-15. doi: 10.1007/s005350300038. J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12673442 Review.
-
Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014 Aug;4(Suppl 3):S74-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.03.045. Epub 2014 Jun 6. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25755615 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Nomogram for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with FOLFOX 4.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 May 1;18(5):1225-1232. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.5.1225. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 28610406 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of total hepatocellular cancer lifespan, including both clinically evident and preclinical development, using combined network phenotyping strategy and fisher information analysis.Semin Oncol. 2015 Apr;42(2):339-46. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.12.025. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Semin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25843738 Free PMC article.
-
The association between pretreatment serum alkaline phosphatase and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(11):e19438. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019438. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32176073 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting the recurrence and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: a retrospective study of 601 Chinese patients.Clin Transl Oncol. 2016 Aug;18(8):831-40. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1446-0. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26577107
-
The Impact of Infections in Patients Treated with Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 23;13(17):4994. doi: 10.3390/jcm13174994. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lei HJ, Chau GY, Lui WY, Tsay SH, King KL, et al. (2006) Prognostic value and clinical relevance of the 6th Edition 2002 American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 203: 426–435. - PubMed
-
- Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, et al. (1985) Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer 56: 918–928. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Bru C, Bruix J (1999) Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: the BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis 19: 329–338. - PubMed
-
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology 28: 751–755. - PubMed
-
- Prospective validation of the CLIP score: a new prognostic system for patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators. Hepatology 31: 840–845. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

