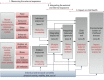
The human early-life exposome (HELIX): project rationale and design
- PMID: 24610234
- PMCID: PMC4048258
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1307204
The human early-life exposome (HELIX): project rationale and design
Abstract
Background: Developmental periods in early life may be particularly vulnerable to impacts of environmental exposures. Human research on this topic has generally focused on single exposure-health effect relationships. The "exposome" concept encompasses the totality of exposures from conception onward, complementing the genome.
Objectives: The Human Early-Life Exposome (HELIX) project is a new collaborative research project that aims to implement novel exposure assessment and biomarker methods to characterize early-life exposure to multiple environmental factors and associate these with omics biomarkers and child health outcomes, thus characterizing the "early-life exposome." Here we describe the general design of the project.
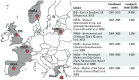
Methods: In six existing birth cohort studies in Europe, HELIX will estimate prenatal and postnatal exposure to a broad range of chemical and physical exposures. Exposure models will be developed for the full cohorts totaling 32,000 mother-child pairs, and biomarkers will be measured in a subset of 1,200 mother-child pairs. Nested repeat-sampling panel studies (n = 150) will collect data on biomarker variability, use smartphones to assess mobility and physical activity, and perform personal exposure monitoring. Omics techniques will determine molecular profiles (metabolome, proteome, transcriptome, epigenome) associated with exposures. Statistical methods for multiple exposures will provide exposure-response estimates for fetal and child growth, obesity, neurodevelopment, and respiratory outcomes. A health impact assessment exercise will evaluate risks and benefits of combined exposures.
Conclusions: HELIX is one of the first attempts to describe the early-life exposome of European populations and unravel its relation to omics markers and health in childhood. As proof of concept, it will form an important first step toward the life-course exposome.
Conflict of interest statement
N.A. is employed by Sensing & Control Systems SL, Igualada, Spain. L.B. is employed by Hylobates Consulting S.R.L., Rome, Italy. The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
The HELIX Project: tracking the exposome in real time.Environ Health Perspect. 2014 Jun;122(6):A169. doi: 10.1289/ehp.122-A169. Environ Health Perspect. 2014. PMID: 24892972 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry; 2000. Manual for the ASEBA Preschool Forms and Profiles.
-
- Bartell SM, Griffith WC, Faustman EM. Temporal error in biomarker-based mean exposure estimates for individuals. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 2004;14:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Beaudouin R, Micallef S, Brochot C. A stochastic whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to assess the impact of inter-individual variability on tissue dosimetry over the human lifespan. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;57(1):103–116. - PubMed
-
- Beelen R, Hoek G, Vienneau D, Eeftens M, Dimakopoulou K, Pedeli X, et al. Development of NO2 and NOx land use regression models for estimating air pollution exposure in 36 study areas in Europe—The ESCAPE project. Atmos Environ. 2013;72:10–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials