Transglutaminase 2 inhibitor abrogates renal cell carcinoma in xenograft models
- PMID: 24610445
- PMCID: PMC11824106
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-014-1623-5
Transglutaminase 2 inhibitor abrogates renal cell carcinoma in xenograft models
Abstract
Purpose: To test whether transglutaminase 2 (TGase 2) inhibitor GK921 alone reverses renal cell carcinoma (RCC) tumor growth. RCC is resistant to both radiation and chemotherapy, and the prognosis remains poor. Despite the recent therapeutic success of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition in RCC, approximately one-third of RCC patients develop metastatic disease. The expression of TGase 2 is markedly increased in most RCC cell lines, as well as in clinical samples.
Methods: Previously, we introduced the quinoxaline derivative GK13 as a lead compound for TGase 2 inhibitor. The inhibitory effect of GK13 on TGase 2 was improved in GK921 (3-(phenylethynyl)-2-(2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)pyrido[3,2-b]pyrazine). GK921 efficacy was tested using sulforhodamine in vitro as well as a xenograft tumor models using ACHN and CAKI-1 RCC cells.
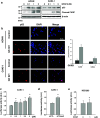
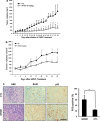
Results: GK921 showed cytotoxicity to RCC (average GI50 in eight RCC cell lines: 0.905 μM). A single treatment with GK921 almost completely reduced tumor growth by stabilizing p53 in the ACHN and CAKI-1 preclinical xenograft tumor models.
Conclusion: TGase 2 inhibitor GK921 abrogates RCC growth in xenograft tumor models, suggesting the possibility of a new therapeutic approach to RCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH, Sherman PM, Holko M, Yefanov A, Lee H, Zhang N, Robertson CL, Serova N, Davis S, Soboleva A (2013) NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets-update. Nucl Acids Res 41(Database issue):D991–D995. doi:10.1093/nar/gks1193 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berglind H, Pawitan Y, Kato S, Ishioka C, Soussi T (2008) Analysis of p53 mutation status in human cancer cell lines: a paradigm for cell line cross-contamination. Cancer Biol Ther 7(5):699–708. doi:10.4161/cbt.7.5.5712 - PubMed
-
- Choueiri TK (2011) VEGF inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: current therapies and future perspective. Curr Clin Pharmacol 6(3):164–168 - PubMed
-
- Delhase M, Kim SY, Lee H, Naiki-Ito A, Chen Y, Ahn ER, Murata K, Kim SJ, Lautsch N, Kobayashi KS, Shirai T, Karin M, Nakanishi M (2012) TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) controls cell survival through PAI-2/serpinB2 and transglutaminase 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(4):E177–E186. doi:10.1073/pnas.1119296109 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gong YD, Lee T (2010) Combinatorial syntheses of five-membered ring heterocycles using carbon disulfide and a solid support. J Comb Chem 12(4):393–409. doi:10.1021/cc100049u - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

