Genome sequence of "Candidatus Walczuchella monophlebidarum" the flavobacterial endosymbiont of Llaveia axin axin (Hemiptera: Coccoidea: Monophlebidae)
- PMID: 24610838
- PMCID: PMC3971599
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evu049
Genome sequence of "Candidatus Walczuchella monophlebidarum" the flavobacterial endosymbiont of Llaveia axin axin (Hemiptera: Coccoidea: Monophlebidae)
Abstract
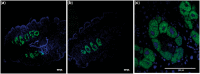
Scale insects (Hemiptera: Coccoidae) constitute a very diverse group of sap-feeding insects with a large diversity of symbiotic associations with bacteria. Here, we present the complete genome sequence, metabolic reconstruction, and comparative genomics of the flavobacterial endosymbiont of the giant scale insect Llaveia axin axin. The gene repertoire of its 309,299 bp genome was similar to that of other flavobacterial insect endosymbionts though not syntenic. According to its genetic content, essential amino acid biosynthesis is likely to be the flavobacterial endosymbiont's principal contribution to the symbiotic association with its insect host. We also report the presence of a γ-proteobacterial symbiont that may be involved in waste nitrogen recycling and also has amino acid biosynthetic capabilities that may provide metabolic precursors to the flavobacterial endosymbiont. We propose "Candidatus Walczuchella monophlebidarum" as the name of the flavobacterial endosymbiont of insects from the Monophlebidae family.
Keywords: comparative genomics; scale insect; symbiosis; γ-Proteobacteria.
Figures



References
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control. 1974;19:716–723.
-
- Ben-Dov Y. A systematic catalogue of the scale insect family Margarodidae (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) of the world. Wimborne (UK): Intercept Ltd; 2005.
-
- de Sousa Araújo TA, de Almeida e Castro VT, de Amorim EL, de Albuquerque UP. Habitat influence on antioxidant activity andtannin concentrations of Spondias tuberosa. Pharm Biol. 2012;50:754–759. - PubMed
-
- Dhami MK, Turner AP, Deines P, Beggs JR, Taylor MW. Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of a bacterial symbiosis in the ecologically important scale insect family Coelostomidiidae. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2012;81:537–546. - PubMed
-
- Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P. Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res. 1998;8:195–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

