Calligraphy and meditation for stress reduction: an experimental comparison
- PMID: 24611024
- PMCID: PMC3928403
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S55743
Calligraphy and meditation for stress reduction: an experimental comparison
Abstract
Background: Chinese calligraphic handwriting (CCH) has demonstrated a new role in health and therapy. Meanwhile, meditation is an traditional and effective method for coping with stress and staying healthy. This study compared the effectiveness of CCH and meditation as distinctive and parallel stress reduction interventions.
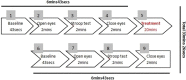
Methods: Thirty graduate students and academic staff members in Taiwan who suffered from stress were selected by the General Health Questionnaire and randomly assigned to one of three treatment groups, ie, a CCH group, a meditation group, or a control group, for 8 consecutive weeks. Changes in physiological parameters were measured before, during, and after treatment.
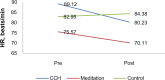
Results: CCH and meditation showed their strength in the respective indices of stress. There was a significant difference in respiratory rate, heart rate, and electromyographic scores between the groups. Comparing pre- and post-effects, a decrease in heart rate and an increase in skin temperature was seen in subjects who practiced CCH. Increased skin temperature and decreased respiratory rate were also seen in subjects who practiced meditation, along with reduced muscle tension and heart rate.
Conclusion: CCH and meditation have good effects in stress reduction. CCH is a particularly promising new approach to reducing stress.
Keywords: calligraphic handwriting; intervention; meditation; stress reduction.
Figures



References
-
- Kao HSR. Chinese Calligraphy Therapy. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press; 2000.
-
- Kao HSR, Chen CC, Chang TM. The effect of calligraphy practice on character recognition reaction time among children with ADHD disorder. In: Roth R, editor. Psychologists Facing the Challenge of a Global Culture with Human Rights and Mental Health; Presented at the 55th Annual Convention of the Council of Psychologists; Graz, Austria. July 14–18, 1997.
-
- Kao HSR. Chinese calligraphy handwriting for health and rehabilitation of the elderly; Presented at the Second World Congress of the International Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine; Prague, Czech Republic. May 18–22, 2003.
-
- Kao HSR, Gao D, Wang M. Brush handwriting treatment of cognitive deficiencies in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21(Suppl 1):14.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

