Mindfulness-based treatment to prevent addictive behavior relapse: theoretical models and hypothesized mechanisms of change
- PMID: 24611847
- PMCID: PMC5441879
- DOI: 10.3109/10826084.2014.891845
Mindfulness-based treatment to prevent addictive behavior relapse: theoretical models and hypothesized mechanisms of change
Abstract
Mindfulness-based treatments are growing in popularity among addiction treatment providers, and several studies suggest the efficacy of incorporating mindfulness practices into the treatment of addiction, including the treatment of substance use disorders and behavioral addictions (i.e., gambling). The current paper provides a review of theoretical models of mindfulness in the treatment of addiction and several hypothesized mechanisms of change. We provide an overview of mindfulness-based relapse prevention (MBRP), including session content, treatment targets, and client feedback from participants who have received MBRP in the context of empirical studies. Future research directions regarding operationalization and measurement, identifying factors that moderate treatment effects, and protocol adaptations for specific populations are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the article.
This research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Grant R01 DA025764-01A1 (G. Alan Marlatt and Sarah Bowen, Principal Investigators).
Figures
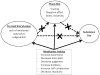
References
-
- Alcoholics Anonymous World Services. Twelve steps and twelve traditions. New York, NY: A. A. Grapevine, Inc; 1952.
-
- Baer RA. Measure mindfulness. Contemporary Buddhism. 2011;12(1):241–261.
-
- Baekland F, Lundwall L. Dropping out of treatment: A critical review. Psychological Bulletin. 1975;82:738–783. - PubMed
-
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Hopkins J, Krietemeyer J, Toney L. Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment. 2006;13:27–45. - PubMed
-
- Biegel BM, Brown KW, Shapiro SL, Shubert CM. Mindfulness-based stress reduction for the treatment of adolescent psychiatric outpatients: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Consulting Clinical Psychology. 2009;77(5):855–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
