Developing regional genetic counseling for southern Chinese with nonsyndromic hearing impairment: a unique mutational spectrum
- PMID: 24612839
- PMCID: PMC3975227
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-64
Developing regional genetic counseling for southern Chinese with nonsyndromic hearing impairment: a unique mutational spectrum
Abstract
Background: Racial and regional factors are important for the clinical diagnosis of non-syndromic hearing impairment. Comprehensive genetic analysis of deaf patients in different regions of China must be performed to provide effective genetic counseling. To evaluate the mutational spectrum of south Chinese families, we performed genetic analysis for non-syndromic hearing impairment in this population.
Methods: Complete clinical evaluations were performed on 701 unrelated patients with non-syndromic hearing impairment from six provinces in south China. Each subject was screened for common mutations, including SLC26A4 c.IVS7-2A > G, c.2168A > G; mitochondrial DNA m.1555A > G, m.1494C > T, m.7444G > A, m.7445A > G; GJB3 c.538C > T, c.547G > A; and WFS1 c.1901A > C, using pyrosequencing. GJB2 and SLC26A4 coding region mutation detection were performed using Sanger sequencing.
Results: Genetic analysis revealed that among the etiology of non-syndromic hearing impairment, GJB2, SLC26A4, and mitochondrial m.1555A > G mutations accounted for 18.0%, 13.1%, and 0.9%, respectively. Common mutations included GJB2 c.235delC, c.109G > A, SLC26A4 c.IVS7-2A > G, c.1229 T > C, and mitochondrial m.1555A > G. The total mutation rate was 45.1% in all patients examined in south China. Overall, the clear contribution of GJB2, SLC26A4, and mitochondrial m.1555A > G to the etiology of the non-syndromic deafness population in south China was 32.0%.
Conclusions: Our study is the first genetic analysis of non-syndromic hearing impairment in south China, and revealed that a clear genetic etiology accounted for 32.0% of non-syndromic hearing cases in patients from these regions. The mutational spectrum of non-syndromic hearing impairment in the south Chinese population provides useful and targeted information to aid in genetic counseling.
Figures


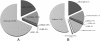
References
-
- Gabriel H, Kupsch P, Sudendey J, Winterhager E, Jahnke K, Lautermann J. Mutations in the connexin26/GJB2 gene are the most common event in non-syndromic hearing loss among the German population. Hum Mutat. 2001;17:521–522. - PubMed
-
- Dai P, Yu F, Han B, Wu H, Yuan YY, Li Q, Wang GJ, Liu X, He J, Huang DL, Kang DY, Zhang X, Yuan HJ, Leejun CW, Han DY. Features of nationwide distribution and frequency of a common gap junction beta-2 gene mutation in China. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007;42:804–808. in Chinese. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

