De novo formation of insulin-producing "neo-β cell islets" from intestinal crypts
- PMID: 24613355
- PMCID: PMC4245054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.02.013
De novo formation of insulin-producing "neo-β cell islets" from intestinal crypts
Abstract
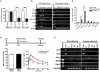
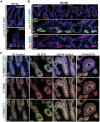
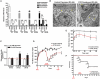
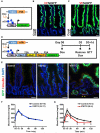
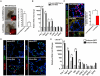
The ability to interconvert terminally differentiated cells could serve as a powerful tool for cell-based treatment of degenerative diseases, including diabetes mellitus. To determine which, if any, adult tissues are competent to activate an islet β cell program, we performed an in vivo screen by expressing three β cell "reprogramming factors" in a wide spectrum of tissues. We report that transient intestinal expression of these factors-Pdx1, MafA, and Ngn3 (PMN)-promotes rapid conversion of intestinal crypt cells into endocrine cells, which coalesce into "neoislets" below the crypt base. Neoislet cells express insulin and show ultrastructural features of β cells. Importantly, intestinal neoislets are glucose-responsive and able to ameliorate hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Moreover, PMN expression in human intestinal "organoids" stimulates the conversion of intestinal epithelial cells into β-like cells. Our results thus demonstrate that the intestine is an accessible and abundant source of functional insulin-producing cells.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Carey BW, Markoulaki S, Hanna JH, Faddah DA, Buganim Y, Kim J, Ganz K, Steine EJ, Cassady JP, Creyghton MP, et al. Reprogramming factor stoichiometry influences the epigenetic state and biological properties of induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9:588–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01-DK091415/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK089536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK083355/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP2-DK083111/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 DK083111/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK077445/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083355/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK091415/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

