2-Aminothiazolones as anti-HIV agents that act as gp120-CD4 inhibitors
- PMID: 24614386
- PMCID: PMC4068444
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02739-13
2-Aminothiazolones as anti-HIV agents that act as gp120-CD4 inhibitors
Abstract
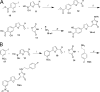
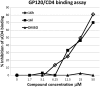
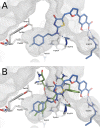
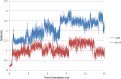
We report here the synthesis of 2-aminothiazolones along with their biological properties as novel anti-HIV agents. Such compounds have proven to act through the inhibition of the gp120-CD4 protein-protein interaction that occurs at the very early stage of the HIV-1 entry process. No cytotoxicity was found for these compounds, and broad antiviral activities against laboratory strains and pseudotyped viruses were documented. Docking simulations have also been applied to predict the mechanism, at the molecular level, by which the inhibitors were able to interact within the Phe43 cavity of HIV-1 gp120. Furthermore, a preliminary absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) evaluation was performed. Overall, this study led the basis for the development of more potent HIV entry inhibitors.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- De Luca A, Dunn D, Zazzi M, Camacho R, Torti C, Fanti I, Kaiser R, Sonnerborg A, Codoñer FM, Van Laethem K, Vandamme AM, Bansi L, Ghisetti V, van de Vijver DA, Asboe D, Prosperi MC, Di Giambenedetto S, SEHERE Collaboration in Chain 2013. Declining prevalence of HIV-1 drug resistance in antiretroviral treatment-exposed individuals in Western Europe. J. Infect. Dis. 207:1216–1220. 10.1093/infdis/jit017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

