The Vitamin D Antenatal Asthma Reduction Trial (VDAART): rationale, design, and methods of a randomized, controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy for the primary prevention of asthma and allergies in children
- PMID: 24614387
- PMCID: PMC4086903
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2014.02.006
The Vitamin D Antenatal Asthma Reduction Trial (VDAART): rationale, design, and methods of a randomized, controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy for the primary prevention of asthma and allergies in children
Abstract
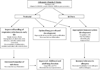
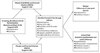
There is intense interest in the role of vitamin D in the development of asthma and allergies. However, studies differ on whether a higher vitamin D intake or status in pregnancy or at birth is protective against asthma and allergies. To address this uncertainty, the Vitamin D Antenatal Asthma Reduction Trial (VDAART) was developed. VDAART is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation in pregnant women to determine whether prenatal supplementation can prevent the development of asthma and allergies in women's offspring. A secondary aim is to determine whether vitamin D supplementation can prevent the development of pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, and gestational diabetes. Women were randomized to the treatment arm of 4000IU/day of vitamin D3 plus a daily multivitamin that contained 400IU of vitamin D3 or the placebo arm of placebo plus a multivitamin that contained 400IU daily of vitamin D3. Women who were between the gestational ages of 10 and 18 weeks were randomized from three clinical centers across the United States - Boston Medical Center, Washington University in St. Louis, and Kaiser Permanente Southern California Region (San Diego, CA). Supplementation took place throughout pregnancy. Monthly monitoring of urinary calcium to creatinine ratio was performed in addition to medical record review for adverse events. Offspring are being evaluated quarterly through questionnaires and yearly during in-person visits until the 3rd birthday of the child. Ancillary studies will investigate neonatal T-regulatory cell function, maternal vaginal flora, and maternal and child intestinal flora.
Keywords: Allergy; Asthma; Developmental origins; Prenatal; Randomized controlled trial; Vitamin D.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Can we prevent childhood asthma before birth? Summary of the VDAART results so far.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016 Oct;10(10):1039-40. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2016.1227257. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 27564842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yunginger JW, Reed CE, O'Connell EJ, Melton LJ, 3rd, O'Fallon WM, Silverstein MD. A community-based study of the epidemiology of asthma. Incidence rates, 1964–1983. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146(4):888–894. - PubMed
-
- King ME, Mannino DM, Holguin F. Risk factors for asthma incidence. A review of recent prospective evidence. Panminerva Med. 2004;46(2):97–110. - PubMed
-
- Mannino DM, Homa DM, Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Gwynn C, Redd SC. Surveillance for asthma--United States, 1980–1999. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2002;51(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality, 2002. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2004.
-
- Smith DH, Malone DC, Lawson KA, Okamoto LJ, Battista C, Saunders WB. A national estimate of the economic costs of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(3 Pt 1):787–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

