Crystal structures of the human RNA demethylase Alkbh5 reveal basis for substrate recognition
- PMID: 24616105
- PMCID: PMC4002068
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546168
Crystal structures of the human RNA demethylase Alkbh5 reveal basis for substrate recognition
Abstract
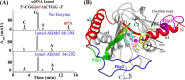
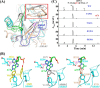
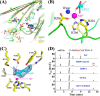
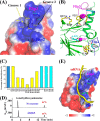
N(6)-Methylation of adenosine is the most ubiquitous and abundant modification of nucleoside in eukaryotic mRNA and long non-coding RNA. This modification plays an essential role in the regulation of mRNA translation and RNA metabolism. Recently, human AlkB homolog 5 (Alkbh5) and fat mass- and obesity-associated protein (FTO) were shown to erase this methyl modification on mRNA. Here, we report five high resolution crystal structures of the catalytic core of Alkbh5 in complex with different ligands. Compared with other AlkB proteins, Alkbh5 displays several unique structural features on top of the conserved double-stranded β-helix fold typical of this protein family. Among the unique features, a distinct "lid" region of Alkbh5 plays a vital role in substrate recognition and catalysis. An unexpected disulfide bond between Cys-230 and Cys-267 is crucial for the selective binding of Alkbh5 to single-stranded RNA/DNA by bringing a "flipping" motif toward the central β-helix fold. We generated a substrate binding model of Alkbh5 based on a demethylation activity assay of several structure-guided site-directed mutants. Crystallographic and biochemical studies using various analogs of α-ketoglutarate revealed that the active site cavity of Alkbh5 is much smaller than that of FTO and preferentially binds small molecule inhibitors. Taken together, our findings provide a structural basis for understanding the substrate recognition specificity of Alkbh5 and offer a foundation for selective drug design against AlkB members.
Keywords: AlkB; Alkbh5; Crystal Structure; Drug Design; Enzyme Inhibitors; RNA Modification; Substrate Recognition; m6A Demethylase; mRNA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structures of human ALKBH5 demethylase reveal a unique binding mode for specific single-stranded N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17299-311. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.550350. Epub 2014 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24778178 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of human RNA N⁶-methyladenine demethylase ALKBH5 provides insights into its mechanisms of nucleic acid recognition and demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(7):4741-54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku085. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24489119 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the RNA demethylase ALKBH5 from zebrafish.FEBS Lett. 2014 Mar 18;588(6):892-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.021. Epub 2014 Feb 20. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24561204 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic RNA modifications in disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014 Jun;26:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014. PMID: 25005745 Review.
-
Role of the m6A demethylase ALKBH5 in gastrointestinal tract cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Feb;55(2):22. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5463. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39611478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of N6-methyladenosine modification on metabolic reprogramming in digestive tract tumors.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 11;10(2):e24414. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24414. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALKBH5 regulates anti-PD-1 therapy response by modulating lactate and suppressive immune cell accumulation in tumor microenvironment.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 18;117(33):20159-20170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918986117. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32747553 Free PMC article.
-
Small changes, big implications: The impact of m6A RNA methylation on gene expression in pluripotency and development.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Sep;1862(9):194402. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 31325527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 in cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Jan 21;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01224-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35063010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-Molecule Targeting of Oncogenic FTO Demethylase in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2019 Apr 15;35(4):677-691.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.03.006. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 30991027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei C., Gershowitz A., Moss B. (1975) N6,O2′-dimethyladenosine a novel methylated ribonucleoside next to the 5′ terminal of animal cell and virus mRNAs. Nature 257, 251–253 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

