Childhood abuse is associated with methylation of multiple loci in adult DNA
- PMID: 24618023
- PMCID: PMC4007631
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-7-13
Childhood abuse is associated with methylation of multiple loci in adult DNA
Abstract
Background: Childhood abuse is associated with increased adult disease risk, suggesting that processes acting over the long-term, such as epigenetic regulation of gene activity, may be involved. DNA methylation is a critical mechanism in epigenetic regulation. We aimed to establish whether childhood abuse was associated with adult DNA methylation profiles.
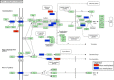
Methods: In 40 males from the 1958 British Birth Cohort we compared genome-wide promoter DNA methylation in blood taken at 45y for those with, versus those without, childhood abuse (n = 12 vs 28). We analysed the promoter methylation of over 20,000 genes and 489 microRNAs, using MeDIP (methylated DNA immunoprecipitation) in triplicate.
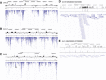
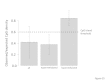
Results: We found 997 differentially methylated gene promoters (311 hypermethylated and 686 hypomethylated) in association with childhood abuse and these promoters were enriched for genes involved in key cell signaling pathways related to transcriptional regulation and development. Using bisulfite-pyrosequencing, abuse-associated methylation (MeDIP) at the metalloproteinase gene, PM20D1, was validated and then replicated in an additional 27 males. Abuse-associated methylation was observed in 39 microRNAs; in 6 of these, the hypermethylated state was consistent with the hypomethylation of their downstream gene targets. Although distributed across the genome, the differentially methylated promoters associated with child abuse clustered in genome regions of at least one megabase. The observations for child abuse showed little overlap with methylation patterns associated with socioeconomic position.
Conclusions: Our observed genome-wide methylation profiles in adult DNA associated with childhood abuse justify the further exploration of epigenetic regulation as a mediating mechanism for long-term health outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Anda RF, Whitfield CL, Felitti VJ, Chapman D, Edwards VJ, Dube SR, Williamson DF. Adverse childhood experiences, alcoholic parents, and later risk of alcoholism and depression. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;7(8):1001–1009. - PubMed
-
- Dube SR, Miller JW, Brown DW, Giles WH, Felitti VJ, Dong M, Anda RF. Adverse childhood experiences and the association with ever using alcohol and initiating alcohol use during adolescence. J Adolesc Health. 2006;7(4):444. e441-410. - PubMed
-
- Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, Williamson DF, Spitz AM, Edwards V, Koss MP, Marks JS. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) study. Am J Prev Med. 1998;7(4):245–258. doi: 10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00017-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

