Heme-induced neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the pathogenesis of sickle cell disease
- PMID: 24620350
- PMCID: PMC4055928
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-529982
Heme-induced neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the pathogenesis of sickle cell disease
Abstract
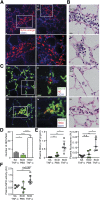
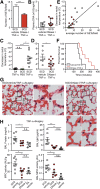
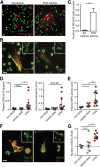
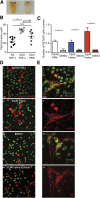
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is characterized by recurring episodes of vascular occlusion in which neutrophil activation plays a major role. The disease is associated with chronic hemolysis with elevated cell-free hemoglobin and heme. The ensuing depletion of heme scavenger proteins leads to nonspecific heme uptake and heme-catalyzed generation of reactive oxygen species. Here, we have identified a novel role for heme in the induction of neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation in SCD. NETs are decondensed chromatin decorated by granular enzymes and are released by activated neutrophils. In humanized SCD mice, we have detected NETs in the lungs and soluble NET components in plasma. The presence of NETs was associated with hypothermia and death of these mice, which could be prevented and delayed, respectively, by dismantling NETs with DNase I treatment. We have identified heme as the plasma factor that stimulates neutrophils to release NETs in vitro and in vivo. Increasing or decreasing plasma heme concentrations can induce or prevent, respectively, in vivo NET formation, indicating that heme plays a crucial role in stimulating NET release in SCD. Our results thus suggest that NETs significantly contribute to SCD pathogenesis and can serve as a therapeutic target for treating SCD.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
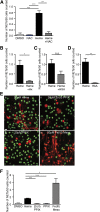
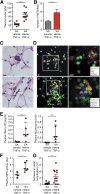

Comment in
-
Erythroid DAMPs drive inflammation in SCD.Blood. 2014 Jun 12;123(24):3689-90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-563874. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24926069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reiter CD, Wang X, Tanus-Santos JE, et al. Cell-free hemoglobin limits nitric oxide bioavailability in sickle-cell disease. Nat Med. 2002;8(12):1383–1389. - PubMed
-
- Chirico EN, Pialoux V. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of sickle cell disease. IUBMB Life. 2012;64(1):72–80. - PubMed
-
- Lard LR, Mul FP, de Haas M, Roos D, Duits AJ. Neutrophil activation in sickle cell disease. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;66(3):411–415. - PubMed
-
- Amer J, Ghoti H, Rachmilewitz E, Koren A, Levin C, Fibach E. Red blood cells, platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils of patients with sickle cell disease exhibit oxidative stress that can be ameliorated by antioxidants. Br J Haematol. 2006;132(1):108–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

