Cardiovascular effects of phentermine and topiramate: a new drug combination for the treatment of obesity
- PMID: 24621808
- PMCID: PMC4011567
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000145
Cardiovascular effects of phentermine and topiramate: a new drug combination for the treatment of obesity
Abstract
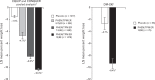
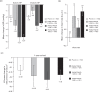
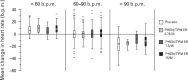
Weight loss can reduce the increased cardiovascular risk associated with obesity. Pharmacotherapy is a recognized weight loss treatment option; however, cardiovascular safety issues with some previous weight loss drugs raise concerns for newly approved pharmacotherapies. Phentermine is approved for short-term obesity treatment in conjunction with lifestyle modifications, but is commonly used chronically. Topiramate, approved for treating epilepsy and preventing migraines, also induces weight loss. A single-dose combination of low-dose phentermine and topiramate extended-release was recently approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for the chronic treatment of overweight/obese adults. This review summarizes and evaluates the cardiovascular risk/benefit profile associated with phentermine and topiramate, individually and in combination. Cardiovascular data associated with long-term use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release indicate that this combination may be a safe and effective option for reducing weight in overweight/obese patients at low-to-intermediate cardiovascular risk.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Obesity and overweight fact sheet No 311. (WWW document); 2013. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html
-
- Nguyen T, Lau DC. The obesity epidemic and its impact on hypertension. Can J Cardiol 2012; 28:326–333 - PubMed
-
- Jordan J, Yumuk V, Schlaich M, Nilsson PM, Zahorska-Markiewicz B, Grassi G, et al. Joint statement of the European Association for the Study of Obesity and the European Society of Hypertension: obesity and difficult to treat arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2012; 30:1047–1055 - PubMed
-
- Gerber Y, Jacobsen SJ, Frye RI, Weston SA, Killian JM, Roger VL. Secular trends in deaths from cardiovascular diseases: a 25-year community study. Circulation 2006; 113:2285–2292 - PubMed
-
- Sytkowski PA, Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB. Changes in risk factors and the decline in mortality from CVD. The Framingham Heart Study. N Engl J Med 1990; 322:1635–1641 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

