Decreased levels of BAG3 in a family with a rare variant and in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 24623017
- PMCID: PMC4296028
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24615
Decreased levels of BAG3 in a family with a rare variant and in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract
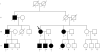
The most common cause of dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure (HF) is ischemic heart disease; however, in a third of all patients the cause remains undefined and patients are diagnosed as having idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (IDC). Recent studies suggest that many patients with IDC have a family history of HF and rare genetic variants in over 35 genes have been shown to be causative of disease. We employed whole-exome sequencing to identify the causative variant in a large family with autosomal dominant transmission of dilated cardiomyopathy. Sequencing and subsequent informatics revealed a novel 10-nucleotide deletion in the BCL2-associated athanogene 3 (BAG3) gene (Ch10:del 121436332_12143641: del. 1266_1275 [NM 004281]) that segregated with all affected individuals. The deletion predicted a shift in the reading frame with the resultant deletion of 135 amino acids from the C-terminal end of the protein. Consistent with genetic variants in genes encoding other sarcomeric proteins there was a considerable amount of genetic heterogeneity in the affected family members. Interestingly, we also found that the levels of BAG3 protein were significantly reduced in the hearts from unrelated patients with end-stage HF undergoing cardiac transplantation when compared with non-failing controls. Diminished levels of BAG3 protein may be associated with both familial and non-familial forms of dilated cardiomyopathy.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Jefferies JLTJ. Dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet. 2010;375:752–762. - PubMed
-
- Judge DP, Johnson NM. Genetic evaluation of familial cardiomyopathy. Journal of cardiovascular translational research. 2008;1:144–154. - PubMed
-
- Morales A, Hershberger RE. Genetic evaluation of dilated cardiomyopathy. Current cardiology reports. 2013;15:375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

