Quantification of deaminase activity-dependent and -independent restriction of HIV-1 replication mediated by APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G through experimental-mathematical investigation
- PMID: 24623435
- PMCID: PMC4019142
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00062-14
Quantification of deaminase activity-dependent and -independent restriction of HIV-1 replication mediated by APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G through experimental-mathematical investigation
Abstract
APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G cytidine deaminases potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication by enzymatically inserting G-to-A mutations in viral DNA and/or impairing viral reverse transcription independently of their deaminase activity. Through experimental and mathematical investigation, here we quantitatively demonstrate that 99.3% of the antiviral effect of APOBEC3G is dependent on its deaminase activity, whereas 30.2% of the antiviral effect of APOBEC3F is attributed to deaminase-independent ability. This is the first report quantitatively elucidating how APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G differ in their anti-HIV-1 modes.
Figures
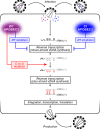
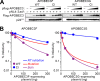
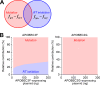

References
-
- Freed EO, Martin MA. 2007. HIVs and their replication, p 2107–2185 In Knipe DM, Howley PM. (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed, vol 2 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

