Development and optimization of a high-throughput assay to measure neutralizing antibodies against Clostridium difficile binary toxin
- PMID: 24623624
- PMCID: PMC4018877
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00038-14
Development and optimization of a high-throughput assay to measure neutralizing antibodies against Clostridium difficile binary toxin
Abstract
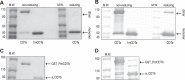
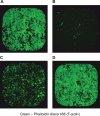
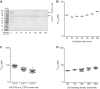
Clostridium difficile strains producing binary toxin, in addition to toxin A (TcdA) and toxin B (TcdB), have been associated with more severe disease and increased recurrence of C. difficile infection in recent outbreaks. Binary toxin comprises two subunits (CDTa and CDTb) and catalyzes the ADP-ribosylation of globular actin (G-actin), which leads to the depolymerization of filamentous actin (F-actin) filaments. A robust assay is highly desirable for detecting the cytotoxic effect of the toxin and the presence of neutralizing antibodies in animal and human sera to evaluate vaccine efficacy. We describe here the optimization, using design-of-experiment (DOE) methodology, of a high-throughput assay to measure the toxin potency and neutralizing antibodies (NAb) against binary toxin. Vero cells were chosen from a panel of cells screened for sensitivity and specificity. We have successfully optimized the CDTa-to-CDTb molar ratio, toxin concentration, cell-seeding density, and sera-toxin preincubation time in the NAb assay using DOE methodology. This assay is robust, produces linear results across serial dilutions of hyperimmune serum, and can be used to quantify neutralizing antibodies in sera from hamsters and monkeys immunized with C. difficile binary toxin-containing vaccines. The assay will be useful for C. difficile diagnosis, for epidemiology studies, and for selecting and optimizing vaccine candidates.
Figures


References
-
- Rupnik M, Pabst S, Rupnik M, von Eichel-Streiber C, Urlaub H, Söling HD. 2005. Characterization of the cleavage site and function of resulting cleavage fragments after limited proteolysis of Clostridium difficile toxin B (TcdB) by host cells. Microbiology 151:199–208. 10.1099/mic.0.27474-0 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

