Potential pathway of anti-inflammatory effect by New Zealand honeys
- PMID: 24623989
- PMCID: PMC3949697
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S45839
Potential pathway of anti-inflammatory effect by New Zealand honeys
Abstract
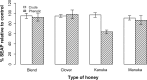
The role of honey in wound healing continues to attract worldwide attention. This study examines the anti-inflammatory effect of four honeys on wound healing, to gauge its efficacy as a treatment option. Isolated phenolics and crude extracts from manuka (Leptospermum scoparium), kanuka (Kunzea ericoides), clover (Trifolium spp.), and a manuka/kanuka blend of honeys were examined. Anti-inflammatory assays were conducted in HEK-Blue™-2, HEK-Blue™-4, and nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD)2-Wild Type (NOD2-WT) cell lines, to assess the extent to which honey treatment impacts on the inflammatory response and whether the effect was pathway-specific. Kanuka honey, and to a lesser extent manuka honey, produced a powerful anti-inflammatory effect related to their phenolic content. The effect was observed in HEK-Blue™-2 cells using the synthetic tripalmitoylated lipopeptide Pam3CysSerLys4 (Pam3CSK4) ligand, suggesting that honey acts specifically through the toll-like receptor (TLR)1/TLR2 signaling pathway. The manuka/kanuka blend and clover honeys had no significant anti-inflammatory effect in any cell line. The research found that kanuka and manuka honeys have an important role in modulating the inflammatory response associated with wound healing, through a pathway-specific effect. The phenolic content of honey correlates with its effectiveness, although the specific compounds involved remain to be determined.
Keywords: Kunzea ericoides; Leptospermum scoparium; Trifolium; clover; inflammatory response; kanuka; manuka; phenolics; wound healing.
Figures

References
-
- Lee DS, Sinno S, Khachemoune A. Honey and wound healing: an overview. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12(3):181–190. - PubMed
-
- Molan PC. Using honey in wound care. IJCA. 2006;3(2):21–24.
-
- Molan PC. The role of honey in the management of wounds. J Wound Care. 1999;8(8):415–418. - PubMed
-
- Mathews KA, Binnington AG. Wound management using honey. Compendium for the Continuing Education of the Practicing Veterinarian. 2002;24(1):53–60.
-
- Subrahmanyam M. Honey dressing versus boiled potato peel in the treatment of burns: a prospective randomized study. Burns. 1996;22(6):491–493. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

