Effect of phenylephrine vs. ephedrine on frontal lobe oxygenation during caesarean section with spinal anesthesia: an open label randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24624090
- PMCID: PMC3940064
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00081
Effect of phenylephrine vs. ephedrine on frontal lobe oxygenation during caesarean section with spinal anesthesia: an open label randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: During caesarean section spinal anesthesia may provoke maternal hypotension that we prevent by administration of phenylephrine and/or ephedrine. Phenylephrine is however reported to reduce the near infrared spectroscopy-determined frontal lobe oxygenation (ScO2) but whether that is the case for patients exposed to spinal anesthesia is not known.
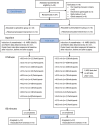
Objectives: To evaluate the impact of phenylephrine vs. ephedrine on ScO2during caesarean section with spinal anesthesia in a single center, open-label parallel-group study with balanced randomization of 24 women (1:1). Secondary aims were to compare the effect of the two drugs on maternal hemodynamics and fetal heart rate.
Intervention: Ephedrine (0.8-3.3 mg/min) vs. phenylephrine infusion (0.02-0.07 mg/min).
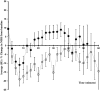
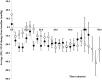
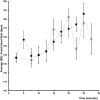
Results: For the duration of surgery, administration of ephedrine maintained ScO2 (compared to baseline +2.1 ± 2.8%; mean ± SE, while phenylephrine reduced ScO2 (-8.6 ± 2.8%; p = 0.005) with a 10.7% difference in ScO2between groups (p = 0.0106). Also maternal heart rate was maintained with ephedrine (+3 ± 3 bpm) but decreased with phenylephrine (-11 ± 3 bpm); difference 14 bpm (p = 0.0053), but no significant difference in mean arterial pressure (p = 0.1904) or CO (p = 0.0683) was observed between groups. The two drugs also elicited an equal increase in fetal heart rate (by 19 ± 3 vs. 18 ± 3 bpm; p = 0.744).
Conclusion: In the choice between phenylephrine and ephedrine for maintenance of blood pressure during caesarean section with spinal anesthesia, ephedrine maintains frontal lobe oxygenation and maternal heart rate with a similar increase in fetal heart rate as elicited by phenylephrine.
Trial registration: Clinical trials NCT 01509521 and EudraCT 2001 006103 35.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01509521.
Keywords: cerebral autoregulation; drug effect; fetal; heart rate; near infrared spectroscopy; vasoconstrictor agents.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

