Bone mineral density changes among HIV-uninfected young adults in a randomised trial of pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir-emtricitabine or placebo in Botswana
- PMID: 24625530
- PMCID: PMC3953113
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090111
Bone mineral density changes among HIV-uninfected young adults in a randomised trial of pre-exposure prophylaxis with tenofovir-emtricitabine or placebo in Botswana
Abstract
Background: Tenofovir-emtricitabine (TDF-FTC) pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has been found to be effective for prevention of HIV infection in several clinical trials. Two studies of TDF PrEP among men who have sex with men showed slight bone mineral density (BMD) loss. We investigated the effect of TDF and the interaction of TDF and hormonal contraception on BMD among HIV-uninfected African men and women.
Method: We evaluated the effects on BMD of using daily oral TDF-FTC compared to placebo among heterosexual men and women aged 18-29 years enrolled in the Botswana TDF2 PrEP study. Participants had BMD measurements at baseline and thereafter at 6-month intervals with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans at the hip, spine, and forearm.
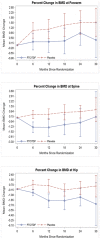
Results: A total of 220 participants (108 TDF-FTC, 112 placebo) had baseline DXA BMD measurements at three anatomic sites. Fifteen (6.8%) participants had low baseline BMD (z-score of <-2.0 at any anatomic site), including 3/114 women (2.6%) and 12/106 men (11.3%) (p = 0.02). Low baseline BMD was associated with being underweight (p = 0.02), having high blood urea nitrogen (p = 0.02) or high alkaline phosphatase (p = 0.03), and low creatinine clearance (p = 0.04). BMD losses of >3.0% at any anatomic site at any time after baseline were significantly greater for the TDF-FTC treatment group [34/68 (50.0%) TDF-FTC vs. 26/79 (32.9%) placebo; p = 0.04]. There was a small but significant difference in the mean percent change in BMD from baseline for TDF-FTC versus placebo at all three sites at month 30 [forearm -0.84% (p = 0.01), spine -1.62% (p = 0.0002), hip -1.51% (p = 0.003)].
Conclusion: Use of TDF-FTC was associated with a small but statistically significant decrease in BMD at the forearm, hip and lumbar spine. A high percentage (6.8%) of healthy Batswana young adults had abnormal baseline BMD Further evaluation is needed of the longer-term use of TDF in HIV-uninfected persons.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00448669.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, Smith DK, Rose CE, et al. (2012) Antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med 367 (5) 423–344. - PubMed
-
- Choopanya K, Martin M, Sangkum U, Mock PA, Leethochawalit M, et al. (2013) Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial - PubMed
-
- Gallant JE, DeJesus E, Arribas JR, Pozniak AL, Gazzard B, et al. (2006) Tenofovir-DF, emtricitabine, and efavirenz vs. zidovudine, lamivudine and efavirenz for HIV. N Engl J Med 354: 251–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous