Disruption of HLA class II antigen presentation in Burkitt lymphoma: implication of a 47,000 MW acid labile protein in CD4+ T-cell recognition
- PMID: 24628049
- PMCID: PMC4080965
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12281
Disruption of HLA class II antigen presentation in Burkitt lymphoma: implication of a 47,000 MW acid labile protein in CD4+ T-cell recognition
Abstract
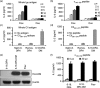
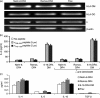
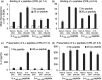
While Burkitt lymphoma (BL) has a well-known defect in HLA class I-mediated antigen presentation, the exact role of BL-associated HLA class II in generating a poor CD4(+) T-cell response remains unresolved. Here, we found that BL cells are deficient in their ability to optimally stimulate CD4(+) T cells via the HLA class II pathway. This defect in CD4(+) T-cell recognition was not associated with low levels of co-stimulatory molecules on BL cells, as addition of external co-stimulation failed to elicit CD4(+) T-cell activation by BL. Further, the defect was not caused by faulty antigen/class II interaction, because antigenic peptides bound with measurable affinity to BL-associated class II molecules. Interestingly, functional class II-peptide complexes were formed at acidic pH 5·5, which restored immune recognition. Acidic buffer (pH 5·5) eluate from BL cells contained molecules that impaired class II-mediated antigen presentation and CD4(+) T-cell recognition. Biochemical analysis showed that these molecules were greater than 30,000 molecular weight in size, and proteinaceous in nature. In addition, BL was found to have decreased expression of a 47,000 molecular weight enolase-like molecule that enhances class II-mediated antigen presentation in B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells, but not in BL cells. These findings demonstrate that BL likely has multiple defects in HLA class II-mediated antigen presentation and immune recognition, which may be exploited for future immunotherapies.
Keywords: Burkitt lymphoma; HLA class II; antigen presentation; enolase-like molecules; immune escape.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
B-Cell Lymphomas Secrete Novel Inhibitory Molecules That Disrupt HLA Class II-Mediated CD4+ T-Cell Recognition.Cells. 2025 Aug 7;14(15):1220. doi: 10.3390/cells14151220. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801653 Free PMC article.
-
HLA class II defects in Burkitt lymphoma: bryostatin-1-induced 17 kDa protein restores CD4+ T-cell recognition.Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:780839. doi: 10.1155/2011/780839. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22162713 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of c-MYC disrupts HLA class II-mediated immune recognition of human B cell tumors.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 15;194(4):1434-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402382. Epub 2015 Jan 16. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25595783 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide binding and antigen presentation by class II histocompatibility glycoproteins.Biopolymers. 1997;43(4):303-22. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1997)43:4<303::AID-BIP4>3.0.CO;2-Z. Biopolymers. 1997. PMID: 9316394 Review.
-
The role of H2-O and HLA-DO in major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted antigen processing and presentation.Immunol Rev. 1999 Dec;172:255-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01370.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10631951 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Defects Impair the HLA Class II Antigen Presentation Capacity of Burkitt Lymphoma.J Clin Cell Immunol. 2016 Aug;7(4):e119. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000e119. Epub 2016 Aug 5. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27747135 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Calpain mediated expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T cells in rodent models of Parkinson's disease.Exp Neurol. 2020 Aug;330:113315. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113315. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32302678 Free PMC article.
-
B-Cell Lymphomas Secrete Novel Inhibitory Molecules That Disrupt HLA Class II-Mediated CD4+ T-Cell Recognition.Cells. 2025 Aug 7;14(15):1220. doi: 10.3390/cells14151220. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801653 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Enolase in Reducing Secondary Damage in Acute Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Neurochem Res. 2017 Oct;42(10):2777-2787. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2291-z. Epub 2017 May 15. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28508172 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Calpain Activation Protects MPTP-Induced Nigral and Spinal Cord Neurodegeneration, Reduces Inflammation, and Improves Gait Dynamics in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Oct;52(2):1054-66. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9255-6. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26108182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biko DM, Anupindi SA, Hernandez A, Kersun L, Bellah R. Childhood Burkitt lymphoma: abdominal and pelvic imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192:1304–15. - PubMed
-
- Ott G, Rosenwald A, Campo E. Understanding MYC-driven aggressive B-cell lymphomas: pathogenesis and classification. Blood. 2013;122:3884–91. - PubMed
-
- Gromminger S, Mautner J, Bornkamm GW. Burkitt lymphoma: the role of Epstein–Barr virus revisited. Br J Haematol. 2012;156:719–29. - PubMed
-
- Brady G, Macarthur GJ, Farrell PJ. Epstein–Barr virus and Burkitt lymphoma. Postgrad Med J. 2008;84:372–7. - PubMed
-
- Perkins AS, Friedberg JW. Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008;2008:341–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

