Human viral oncogenesis: a cancer hallmarks analysis
- PMID: 24629334
- PMCID: PMC3992243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.011
Human viral oncogenesis: a cancer hallmarks analysis
Abstract
Approximately 12% of all human cancers are caused by oncoviruses. Human viral oncogenesis is complex, and only a small percentage of the infected individuals develop cancer, often many years to decades after the initial infection. This reflects the multistep nature of viral oncogenesis, host genetic variability, and the fact that viruses contribute to only a portion of the oncogenic events. In this review, the Hallmarks of Cancer framework of Hanahan and Weinberg (2000 and 2011) is used to dissect the viral, host, and environmental cofactors that contribute to the biology of multistep oncogenesis mediated by established human oncoviruses. The viruses discussed include Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPVs), hepatitis B and C viruses (HBV and HCV, respectively), human T cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1), and Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

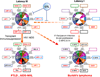


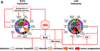


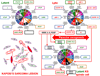
References
-
- Aoki Y, Jaffe ES, Chang Y, Jones K, Teruya-Feldstein J, Moore PS, Tosato G. Angiogenesis and hematopoiesis induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6. Blood. 1999;93:4034–4043. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Tosato G. Interactions between HIV-1 Tat and KSHV. Current topics in microbiology and immunology. 2007;312:309–326. - PubMed
-
- Arzumanyan A, Reis HM, Feitelson MA. Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature reviews Cancer. 2013;13:123–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA 136387/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA104025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA141583/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076535/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136387/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA081135/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA141583/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI073961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI076535/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30AI073961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081135/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA066980/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA066980/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

