Spliced X-box binding protein 1 couples the unfolded protein response to hexosamine biosynthetic pathway
- PMID: 24630721
- PMCID: PMC3959665
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.014
Spliced X-box binding protein 1 couples the unfolded protein response to hexosamine biosynthetic pathway
Abstract
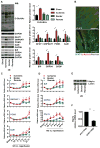
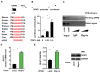
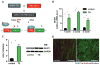
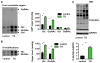
The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) generates uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) for glycan synthesis and O-linked GlcNAc (O-GlcNAc) protein modifications. Despite the established role of the HBP in metabolism and multiple diseases, regulation of the HBP remains largely undefined. Here, we show that spliced X-box binding protein 1 (Xbp1s), the most conserved signal transducer of the unfolded protein response (UPR), is a direct transcriptional activator of the HBP. We demonstrate that the UPR triggers HBP activation via Xbp1s-dependent transcription of genes coding for key, rate-limiting enzymes. We further establish that this previously unrecognized UPR-HBP axis is triggered in a variety of stress conditions. Finally, we demonstrate a physiologic role for the UPR-HBP axis by showing that acute stimulation of Xbp1s in heart by ischemia/reperfusion confers robust cardioprotection in part through induction of the HBP. Collectively, these studies reveal that Xbp1s couples the UPR to the HBP to protect cells under stress.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
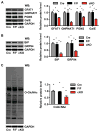
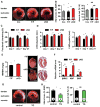
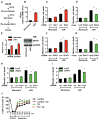
Comment in
-
Sugarcoating ER Stress.Cell. 2014 Mar 13;156(6):1125-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.035. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24630714
-
Finding the missing link between the unfolded protein response and O-GlcNAcylation in the heart.Circ Res. 2014 Aug 29;115(6):546-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.304855. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 25170091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Champattanachai V, Marchase RB, Chatham JC. Glucosamine protects neonatal cardiomyocytes from ischemia-reperfusion injury via increased protein-associated O-GlcNAc. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C178–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK-099110/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HL101254/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102478-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 GM038545/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-100401/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023729/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL-097768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM038545/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007360/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-0980842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120732/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK088761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-080144/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-55758/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-088761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100401/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM-038545/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-072016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080144/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055758/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

