Unified polymerization mechanism for the assembly of ASC-dependent inflammasomes
- PMID: 24630722
- PMCID: PMC4000066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.008
Unified polymerization mechanism for the assembly of ASC-dependent inflammasomes
Abstract
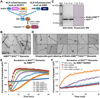
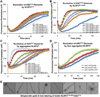
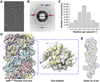
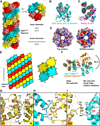
Inflammasomes elicit host defense inside cells by activating caspase-1 for cytokine maturation and cell death. AIM2 and NLRP3 are representative sensor proteins in two major families of inflammasomes. The adaptor protein ASC bridges the sensor proteins and caspase-1 to form ternary inflammasome complexes, achieved through pyrin domain (PYD) interactions between sensors and ASC and through caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD) interactions between ASC and caspase-1. We found that PYD and CARD both form filaments. Activated AIM2 and NLRP3 nucleate PYD filaments of ASC, which, in turn, cluster the CARD of ASC. ASC thus nucleates CARD filaments of caspase-1, leading to proximity-induced activation. Endogenous NLRP3 inflammasome is also filamentous. The cryoelectron microscopy structure of ASC(PYD) filament at near-atomic resolution provides a template for homo- and hetero-PYD/PYD associations, as confirmed by structure-guided mutagenesis. We propose that ASC-dependent inflammasomes in both families share a unified assembly mechanism that involves two successive steps of nucleation-induced polymerization. PAPERFLICK:
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Inflammasome: putting the pieces together.Cell. 2014 Mar 13;156(6):1127-1129. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.038. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24630715
-
Inflammasomes: polymeric assembly.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 May;14(5):287. doi: 10.1038/nri3669. Epub 2014 Apr 11. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24722480 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

