Single-molecule dynamics of enhanceosome assembly in embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 24630727
- PMCID: PMC4040518
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.062
Single-molecule dynamics of enhanceosome assembly in embryonic stem cells
Abstract
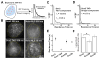
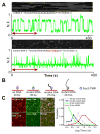
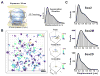
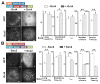
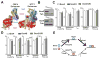
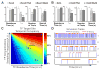
Enhancer-binding pluripotency regulators (Sox2 and Oct4) play a seminal role in embryonic stem (ES) cell-specific gene regulation. Here, we combine in vivo and in vitro single-molecule imaging, transcription factor (TF) mutagenesis, and ChIP-exo mapping to determine how TFs dynamically search for and assemble on their cognate DNA target sites. We find that enhanceosome assembly is hierarchically ordered with kinetically favored Sox2 engaging the target DNA first, followed by assisted binding of Oct4. Sox2/Oct4 follow a trial-and-error sampling mechanism involving 84-97 events of 3D diffusion (3.3-3.7 s) interspersed with brief nonspecific collisions (0.75-0.9 s) before acquiring and dwelling at specific target DNA (12.0-14.6 s). Sox2 employs a 3D diffusion-dominated search mode facilitated by 1D sliding along open DNA to efficiently locate targets. Our findings also reveal fundamental aspects of gene and developmental regulation by fine-tuning TF dynamics and influence of the epigenome on target search parameters.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ben-Tabou de-Leon S, Davidson EH. Gene regulation: gene control network in development. Annual review of biophysics and biomolecular structure. 2007;36:191. - PubMed
-
- Berg OG, Winter RB, von Hippel PH. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 1. Models and theory. Biochemistry. 1981;20:6929–6948. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, et al. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:1106–1117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

