Central neural regulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and energy expenditure
- PMID: 24630813
- PMCID: PMC4016184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.02.007
Central neural regulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and energy expenditure
Abstract
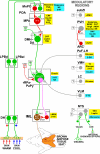
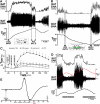
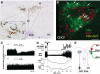
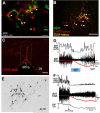
Thermogenesis, the production of heat energy, is the specific, neurally regulated, metabolic function of brown adipose tissue (BAT) and contributes to the maintenance of body temperature during cold exposure and to the elevated core temperature during several behavioral states, including wakefulness, the acute phase response (fever), and stress. BAT energy expenditure requires metabolic fuel availability and contributes to energy balance. This review summarizes the functional organization and neurochemical influences within the CNS networks governing the level of BAT sympathetic nerve activity to produce the thermoregulatory and metabolically driven alterations in BAT thermogenesis and energy expenditure that contribute to overall energy homeostasis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Amini-Sereshki L, Zarrindast MR. Brain stem tonic inhibition of thermoregulation in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1984;247:R154–159. - PubMed
-
- Arruda AP, Milanski M, Romanatto T, Solon C, Coope A, Alberici LC, Festuccia WT, Hirabara SM, Ropelle E, Curi R, Carvalheira JB, Vercesi AE, Velloso LA. Hypothalamic actions of tumor necrosis factor alpha provide the thermogenic core for the wastage syndrome in cachexia. Endocrinology. 2010;151:683–694. - PubMed
-
- Bachman ES, Dhillon H, Zhang CY, Cinti S, Bianco AC, Kobilka BK, Lowell BB. betaAR signaling required for diet-induced thermogenesis and obesity resistance. Science. 2002;297:843–845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
