Epiregulin: roles in normal physiology and cancer
- PMID: 24631357
- PMCID: PMC4037385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.03.005
Epiregulin: roles in normal physiology and cancer
Abstract
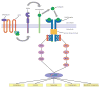
Epiregulin is a 46-amino acid protein that belongs to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family of peptide hormones. Epiregulin binds to the EGF receptor (EGFR/ErbB1) and ErbB4 (HER4) and can stimulate signaling of ErbB2 (HER2/Neu) and ErbB3 (HER3) through ligand-induced heterodimerization with a cognate receptor. Epiregulin possesses a range of functions in both normal physiologic states as well as in pathologic conditions. Epiregulin contributes to inflammation, wound healing, tissue repair, and oocyte maturation by regulating angiogenesis and vascular remodeling and by stimulating cell proliferation. Deregulated epiregulin activity appears to contribute to the progression of a number of different malignancies, including cancers of the bladder, stomach, colon, breast, lung, head and neck, and liver. Therefore, epiregulin and the elements of the EGF/ErbB signaling network that lie downstream of epiregulin appear to be good targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: EGF/ErbB receptors; Epiregulin; Epithelial cell proliferation; Inflammation; Oocyte maturation; Tumor Progression.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Lim H, Dey SK, Das SK. Differential expression of the erbB2 gene in the periimplantation mouse uterus: potential mediator of signaling by epidermal growth factor-like growth factors. Endocrinology. 1997;138:1328–37. - PubMed
-
- Normanno N, Bianco C, De Luca A, Salomon DS. The role of EGF-related peptides in tumor growth. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D685–707. - PubMed
-
- Ocana A, Pandiella A. Targeting HER receptors in cancer. Current pharmaceutical design. 2013;19:808–17. - PubMed
-
- Patel R, Leung HY. Targeting the EGFR-family for therapy: biological challenges and clinical perspective. Current pharmaceutical design. 2012;18:2672–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous