Antiproliferative activities of halogenated thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines
- PMID: 24631358
- PMCID: PMC4565497
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.02.033
Antiproliferative activities of halogenated thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines
Abstract
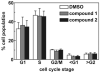
The in vitro evaluation of thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines identified halogenated compounds 1 and 2 with antiproliferative activity against three different cancer cell lines. A structure activity relationship study indicated the necessity of the chlorine at the C4-position for biological activity. The two most active compounds 1 and 2 were found to induce apoptosis in the leukemia L1210 cell line. Additionally, the compounds were screened against a variety of other microbial targets and as a result, selective activity against several fungi was also observed. The synthesis and preliminary biological results are reported herein.
Keywords: Antifungal; Apoptosis; Cytostatic; Heterocyclic chemistry; Thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
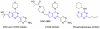


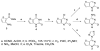

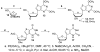

References
-
- Amarnath V, Madhav R. Synthesis. 1974:837.
-
- Lim M-I, Klein RS, Fox JJ. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980;21:1013.
-
- Ren WY, Lim MI, Otter BA, Klein RS. J. Org. Chem. 1982;47:4633.
-
- Lim M-I, Klein RS. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981;22:25.
-
- Lim MI, Ren WY, Otter BA, Klein RS. J. Org. Chem. 1983;48:780.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

