Modeling and preventive measures of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in China
- PMID: 24633146
- PMCID: PMC3987023
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph110303108
Modeling and preventive measures of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in China
Abstract
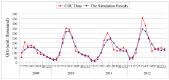
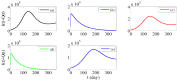
This paper concentrates on the HFMD data of China from March 2009 to December 2012. We set up a mathematical model to fit those data with the goodness of fit and obtain the optimal parameter values of the model. By the Chi-square test of statistical inference, the optimal parameter values of the model are reasonable. We obtained the basic reproductive number of the disease for each year, and it is larger than 1. Thus, we conclude that HFMD will persist in China under the current conditions, so we investigate the preventive measures to control the HFMD. If the preventive measures proposed in our paper were implemented, HFMD would be controlled quickly and the number of infections would decline rapidly over a period of time.
Figures

References
-
- Liu J.L. Threshold dynamics for a HFMD epidemic model with periodic transmission rate. Nonlinear Dyn. 2011;64:89–95. doi: 10.1007/s11071-010-9848-6. - DOI
-
- Schmidt N.J., Lennette E.H., Ho H.H. An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. J. Infect. Dis. 1974;129:304–309. - PubMed
-
- Shindarov L.M., Chumakov M.P., Voroshilova M.K., Bojinov S., Vasilenko S.M., Iordanov I., Kirov I.D., Kamenov E., Leshchinskaya E.V., Mitov G., et al. Epidemiological, clinical and pathomorphological characteristics of epidemic poliomyelitis-like disease caused by enterovirus 71. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1979;23:284–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

