Redox regulation of endothelial cell fate
- PMID: 24633153
- PMCID: PMC4134393
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1598-z
Redox regulation of endothelial cell fate
Abstract
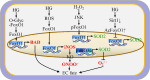
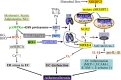
Endothelial cells (ECs) are present throughout blood vessels and have variable roles in both physiological and pathological settings. EC fate is altered and regulated by several key factors in physiological or pathological conditions. Reactive nitrogen species and reactive oxygen species derived from NAD(P)H oxidases, mitochondria, or nitric oxide-producing enzymes are not only cytotoxic but also compose a signaling network in the redox system. The formation, actions, key molecular interactions, and physiological and pathological relevance of redox signals in ECs remain unclear. We review the identities, sources, and biological actions of oxidants and reductants produced during EC function or dysfunction. Further, we discuss how ECs shape key redox sensors and examine the biological functions, transcriptional responses, and post-translational modifications evoked by the redox system in ECs. We summarize recent findings regarding the mechanisms by which redox signals regulate the fate of ECs and address the outcome of altered EC fate in health and disease. Future studies will examine if the redox biology of ECs can be targeted in pathophysiological conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, et al. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998;91:3527–3561. - PubMed
-
- Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun PM. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2004;109:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Spiegelhalter DJ, Georgakopoulos D, Robinson J, Deanfield JE. Aging is associated with endothelial dysfunction in healthy men years before the age-related decline in women. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;24:471–476. - PubMed
-
- Stenvinkel P. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation-is there a link? Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2001;16:1968–1971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

