Reactive carbonyl species in vivo: generation and dual biological effects
- PMID: 24634611
- PMCID: PMC3918703
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/417842
Reactive carbonyl species in vivo: generation and dual biological effects
Abstract
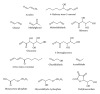
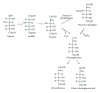
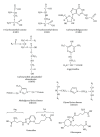
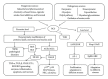
Reactive carbonyls are widespread species in living organisms and mainly known for their damaging effects. The most abundant reactive carbonyl species (RCS) are derived from oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids. Chemical modification of proteins, nucleic acids, and aminophospholipids by RCS results in cytotoxicity and mutagenicity. In addition to their direct toxicity, modification of biomolecules by RCS gives rise to a multitude of adducts and cross links that are increasingly implicated in aging and pathology of a wide range of human diseases. Understanding of the relationship between metabolism of RCS and the development of pathological disorders and diseases may help to develop effective approaches to prevent a number of disorders and diseases. On the other hand, constant persistence of RCS in cells suggests that they perform some useful role in living organisms. The most beneficial effects of RCS are their establishment as regulators of cell signal transduction and gene expression. Since RCS can modulate different biological processes, new tools are required to decipher the precise mechanisms underlying dual effects of RCS.
Figures

References
-
- Gugliucci A. Glycation as the glucose link to diabetic complications. The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association. 2000;100(10):621–634. - PubMed
-
- Uchida K. Role of reactive aldehyde in cardiovascular diseases. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2000;28(12):1685–1696. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414(6865):813–820. - PubMed
-
- Lovell MA, Xie C, Markesbery WR. Acrolein is increased in Alzheimer's disease brain and is toxic to primary hippocampal cultures. Neurobiology of Aging. 2001;22(2):187–194. - PubMed
-
- Picklo MJ, Sr., Montine TJ, Amarnath V, Neely MD. Carbonyl toxicology and Alzheimer's disease. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2002;184(3):187–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

